
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
News Archive
This week we are highlighting the three finest examples of proteomics data made public in 2011. As we
did last year, we are naming the best data in three categories.
 The open access database Antibodypedia, which is linked to on many GPM pages, has changed its root domain name.
This change is part of Antibodypedia's new relationship with the Nature Publishing Group.
The base URL for access to Antibodypedia has changed from:
The open access database Antibodypedia, which is linked to on many GPM pages, has changed its root domain name.
This change is part of Antibodypedia's new relationship with the Nature Publishing Group.
The base URL for access to Antibodypedia has changed from:to "http://www.antibodypedia.com" Any old links to the ".org" domain will no longer function properly. The GPM interface has been updated and any
users of GPM-XE should perform a software update to convert to the new domain name.
Data set of the week: (2011/12/19)
Virus-induced dilated cardiomyopathy is characterized by increased levels of fibrotic extracellular matrix proteins and reduced amounts of energy-producing enzymes. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 91 LC/MS/MS runs from
two dimensional SDS-PAGE spots.
The data was published by
Nishtala K, Phong TQ, Steil L, Sauter M, Salazar MG, Kandolf R, Kroemer HK, Felix SB, Völker U, Klingel K and Hammer E in
Proteomics 2011 11:4310-20 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 91 LC/MS/MS runs from
two dimensional SDS-PAGE spots.
The data was published by
Nishtala K, Phong TQ, Steil L, Sauter M, Salazar MG, Kandolf R, Kroemer HK, Felix SB, Völker U, Klingel K and Hammer E in
Proteomics 2011 11:4310-20 (PubMed).
This data is a good example of what can be done using 2D-SDS PAGE DIGE methods when coupled with
high resolution mass spectrometry-based protein identifications. The analysis showed a small number of proteins per
spot, with good clustering of predicted molecular masses (from the protein sequence) in each sample spot. There
was very signficant contamination of all of the samples with common adventious proteins (H. sapiens KRT1, KRT2, KRT9 and KRT10;
B. taurus α- & κ-casein; and S. scrofa trypsin). The high levels of these proteins made some of
the data analysis a bit tricky: the porcine trypsin in particular contained one peptide that was consistently identified as being from
mouse Try10 while it clearly was from the porcine reagent instead. It would be helpful to the entire field if more effort
was put in to preventing the contamination of polyacrylamide gels.
 Thanks to the release of the Chinese hamster
(Cricetulus griseus) genome
CriGri_1.0, we have been able to add the proteome
of this important model species to the GPM analysis system. While it has been largely replaced as a laboratory
species by M. musculus, it remains important because of the wealth of experience and applications of CHO
cells. This cell line is used for the industrial production of recombinant mammalian proteins as well as
many biomedical studies (searching PubMed with "CHO cells" produces > 32,000 papers). The proteome
currently being used in the GPM was obtained from NCBI's RefSeq repository, however once ENSEMBL has finished creating a
version of the CriGri_1.0 proteome we will review this choice.
Thanks to the release of the Chinese hamster
(Cricetulus griseus) genome
CriGri_1.0, we have been able to add the proteome
of this important model species to the GPM analysis system. While it has been largely replaced as a laboratory
species by M. musculus, it remains important because of the wealth of experience and applications of CHO
cells. This cell line is used for the industrial production of recombinant mammalian proteins as well as
many biomedical studies (searching PubMed with "CHO cells" produces > 32,000 papers). The proteome
currently being used in the GPM was obtained from NCBI's RefSeq repository, however once ENSEMBL has finished creating a
version of the CriGri_1.0 proteome we will review this choice.
 GPMDB has been operating since January 1, 2004. Given this relatively long period of operation, it is
reasonable for users to be concerned that the data they have retrieved about a particular protein
may be out-of-date. During the system's 8 years of operation many of the techniques and instruments
used in proteomics have changed significantly.
GPMDB has been operating since January 1, 2004. Given this relatively long period of operation, it is
reasonable for users to be concerned that the data they have retrieved about a particular protein
may be out-of-date. During the system's 8 years of operation many of the techniques and instruments
used in proteomics have changed significantly.
Thanks to our users and the general community's commitment to making their data openly available, GPMDB has
grown in a peculiar way: the number of peptide identifications in the system has nearly doubled each year. This
doubling (technically "exponential growth") has had the rather happy consequence of keeping the full
data set surprisingly up-to-date. The pie chart below shows the fraction of peptide identifications in the current
database (410,648,190 total) as a function of the calendar year in which the identifications were added.
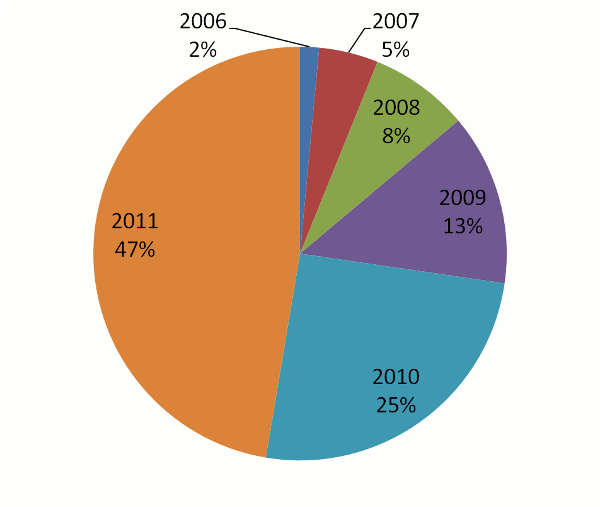
 We are seeking comments and suggestions associated with a draft specification
of a notation for concisely describing observed or predicted protein residue modifications. The purpose of
the notation is to make it easier to specify the types of modifications commonly observed in proteomics, dealling
explicitly with cases inwhich it is inadvisable to claim exactly which residue in a sequence is modified. This notation,
if adopted,
will be used for creating new interfaces to the GPM and other compliant data and information repositories. This RFC will
be active until January 14, 2012.
We are seeking comments and suggestions associated with a draft specification
of a notation for concisely describing observed or predicted protein residue modifications. The purpose of
the notation is to make it easier to specify the types of modifications commonly observed in proteomics, dealling
explicitly with cases inwhich it is inadvisable to claim exactly which residue in a sequence is modified. This notation,
if adopted,
will be used for creating new interfaces to the GPM and other compliant data and information repositories. This RFC will
be active until January 14, 2012.
Data set of the week: (2011/12/12)
Selected reaction monitoring mass spectrometry reveals the dynamics of signaling through the GRB2 adaptor. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 5 LC/MS/MS runs from
affinity purification experiments.
The data was published by
Bisson N, James DA, Ivosev G, Tate SA, Bonner R, Taylor L, Pawson T in
Nat Biotechnol. 2011 29:653-8 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 5 LC/MS/MS runs from
affinity purification experiments.
The data was published by
Bisson N, James DA, Ivosev G, Tate SA, Bonner R, Taylor L, Pawson T in
Nat Biotechnol. 2011 29:653-8 (PubMed).
The five analyses presented here are a good example of the type of MS/MS
identification work that is necessary when setting up a solid SRM/MRM assay for quantitation. There
are several good replicates to establish reproducibility and the MS/MS spectra were generated
on the same type of instrument used to perform the quantitative analysis. The group also paid careful attention
to the chromatography used, which is an under-appreciated necessity for this type of quantitation.
Data set of the week: (2011/12/05)
Phosphoproteomic analysis of Salmonella-infected cells identifies key kinase regulators and SopB-dependent host phosphorylation events. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 9 LC/MS/MS runs collected
using metal oxide capture methods.
The data was published by
Rogers LD, Brown NF, Fang Y, Pelech S, Foster LJ in
Sci Signal. 2011 4:rs9 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 9 LC/MS/MS runs collected
using metal oxide capture methods.
The data was published by
Rogers LD, Brown NF, Fang Y, Pelech S, Foster LJ in
Sci Signal. 2011 4:rs9 (PubMed).
The results derived from this data really show the state-of-the-art when using
an Orbitrap with CID and SILAC quantitation to follow the changes in phosphorylation patterns that
occur during a biological event (in this case Salmonella infection in human cells). All aspects of
the measurement (sample preparation, phosphopeptide enrichment, HPLC and mass spectrometry) were performed
with excellent attention to detail and quality. Any one interested in developing new ways of handling quantitative
proteomics data while simultaneously following a post-translational modification should use these
experiments as a model system for testing their methods.
Data set of the week: (2011/11/27)
A pipeline that integrates the discovery and verification of plasma protein biomarkers reveals candidate markers for cardiovascular disease. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 269 LC/MS/MS runs collected
from multiple replicate runs of human plasma samples.
The data was published by
Addona TA, Shi X, Keshishian H, Mani DR, Burgess M, Gillette MA, Clauser KR, Shen D, Lewis GD, Farrell LA, Fifer MA, Sabatine MS, Gerszten RE, and Carr SA. in
Nat Biotechnol. 2011 29:635-43 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 269 LC/MS/MS runs collected
from multiple replicate runs of human plasma samples.
The data was published by
Addona TA, Shi X, Keshishian H, Mani DR, Burgess M, Gillette MA, Clauser KR, Shen D, Lewis GD, Farrell LA, Fifer MA, Sabatine MS, Gerszten RE, and Carr SA. in
Nat Biotechnol. 2011 29:635-43 (PubMed).
This data represents the maturing of proteomics measurements into a clinical tool. The experiments
were performed using state-of-the-art techniques and allow the in-depth profiling of the proteins present in
clinically-derived plasma samples for the differential diagnosis of cardiovascular events. The combination of
good, solid experimental technique in the plasma measurements in combination with SRM/MRM methods for more
routine monitoring is probably the pattern many clinically-oriented studies will follow for the next few years.
Data set of the week: (2011/11/20)
Systematic and quantitative assessment of the ubiquitin-modified proteome. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 90 LC/MS/MS runs collected
from a series of multidimensional chromatography experiments, using SILAC methods for quantitation.
The data was published by
Kim W, Bennett EJ, Huttlin EL, Guo A, Li J, Possemato A, Sowa ME, Rad R, Rush J, Comb MJ, Harper JW, and Gygi SP. in
Mol Cell. 2011 44(2):325-40 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 90 LC/MS/MS runs collected
from a series of multidimensional chromatography experiments, using SILAC methods for quantitation.
The data was published by
Kim W, Bennett EJ, Huttlin EL, Guo A, Li J, Possemato A, Sowa ME, Rad R, Rush J, Comb MJ, Harper JW, and Gygi SP. in
Mol Cell. 2011 44(2):325-40 (PubMed).
The experiments that generated this data used affinity purification to select
peptides that had been modified by ubiquination. The antibody used recognized the unusual addition of Gly-Gly
to the sidechain of lysine, which only occurs in tryptic peptides generated from ubiquinated proteins. There
have been many studies that used this modification (+114 Da) to identify ubiquitination sites, but these particular
experiments have the largest (and most broadly distributed) set of identified modified lysines in human
proteins currently available. The use of the proteosome inhibitor bortezomib created significantly higher concentrations of
these modified peptides in the cell culture, allowing the antibody pull-down method to be much more effective
than it would have been in untreated cells.
 Some time yesterday (Nov. 17, 2010) the Global Proteome Machine processed its 2,000,000,000th
spectrum. We would like to thank all of the direct contributors to this project,
as well as the investigators who have made there data available through TRANCHE, PRIDE and PeptideAtlas.
The project has long since exceeded its original goal of trying to make proteomics data handling and
information retrieval more systematic (and less proprietary). While proteomics remains a very
secretive discipline in general, there is now an informal group of investigators who see the merits of
making their data public and who regularly make the effort to upload their raw data files for
reanalysis and study. The laboratories of Steve Carr, Steve Gygi, Albert Heck,
Tom Kislinger, Mathias Mann, and Akilesh Pandey have been trend setters in this regard, collectively
making substantial, long-term commitments to contributing their data for use by the broader proteomics
community.
Some time yesterday (Nov. 17, 2010) the Global Proteome Machine processed its 2,000,000,000th
spectrum. We would like to thank all of the direct contributors to this project,
as well as the investigators who have made there data available through TRANCHE, PRIDE and PeptideAtlas.
The project has long since exceeded its original goal of trying to make proteomics data handling and
information retrieval more systematic (and less proprietary). While proteomics remains a very
secretive discipline in general, there is now an informal group of investigators who see the merits of
making their data public and who regularly make the effort to upload their raw data files for
reanalysis and study. The laboratories of Steve Carr, Steve Gygi, Albert Heck,
Tom Kislinger, Mathias Mann, and Akilesh Pandey have been trend setters in this regard, collectively
making substantial, long-term commitments to contributing their data for use by the broader proteomics
community.
Data set of the week: (2011/11/14)
Comparative phosphoproteome profiling reveals a function of the STN8 kinase in fine-tuning of cyclic electron flow (CEF). Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 8 result sets, colllected
from IMAC/TiO2 affinity measurements.
The data was published by
Reiland S, Finazzi G, Endler A, Willig A, Baerenfaller K, Grossmann J, Gerrits B, Rutishauser D, Gruissem W, Rochaix JD, and Baginsky S. in
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 108:12955-60 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 8 result sets, colllected
from IMAC/TiO2 affinity measurements.
The data was published by
Reiland S, Finazzi G, Endler A, Willig A, Baerenfaller K, Grossmann J, Gerrits B, Rutishauser D, Gruissem W, Rochaix JD, and Baginsky S. in
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 108:12955-60 (PubMed).
These results contain some of the best plant phosphorylation information available. The experiments
were very well planned and the analysis was done carefully. Many of the phospho-domains were previously undocumented
and the data was analyzed in a reasonable manner for the resulting manuscript.
Data set of the week: (2011/11/07)
A protein epitope signature Tag (PrEST) library allows SILAC-based absolute quantification and multiplexed determination of protein copy numbers in cell lines. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 138 result sets.
The data was published by
Zeiler M, Straube WL, Lundberg E, Uhlen M, and Mann M. in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 Sep 30 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 138 result sets.
The data was published by
Zeiler M, Straube WL, Lundberg E, Uhlen M, and Mann M. in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 Sep 30 (PubMed).
The data provided by these experiments is a tremendous resource for anyone interested in
proteomics search engine development, testing or statistical analysis. The first 107
LC/MS/MS runs were generated using individual SILAC-labelled PrEST peptides. There are effectively no contaminants, making these
spectra excellent examples to use for determining algorithm sensitive and noise rejection. The remaining sets were large, high quality measurments of
mixtures of either normal PrESTs and SILAC heavy HeLa proteins or
SILAC heavy PrESTs and normal HeLa proteins. The multiple
replicates and well-characterized samples make these runs perfect for determining statistical error rates and
comparing predictions from theoretical distributions to laboratory data.
 The US National Heart, Lung and
Blood Institute
has announced the successful contractors for its national proteomics centers program.
These centers are dispersed around the US and they may have more than one geographical location. The
titles for the Centers and their institutional affiliations are given below — from information posted on
the NIH project web site: The US National Heart, Lung and
Blood Institute
has announced the successful contractors for its national proteomics centers program.
These centers are dispersed around the US and they may have more than one geographical location. The
titles for the Centers and their institutional affiliations are given below — from information posted on
the NIH project web site:
Data set of the week: (2011/10/30)
Proteome-wide mapping of the Drosophila acetylome demonstrates a high degree of conservation of lysine acetylation. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 46 LC/MS/MS runs,
that were enriched in acetylated lysine.
The data was published by
Weinert BT, Wagner SA, Horn H, Henriksen P, Liu WR, Olsen JV, Jensen LJ, and Choudhary C. in
Sci Signal. 2011 4:ra48 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 46 LC/MS/MS runs,
that were enriched in acetylated lysine.
The data was published by
Weinert BT, Wagner SA, Horn H, Henriksen P, Liu WR, Olsen JV, Jensen LJ, and Choudhary C. in
Sci Signal. 2011 4:ra48 (PubMed).
The MS/MS data generated for this paper was first-rate, using Higher-energy Collisional Dissociation
(HCD) and high accuracy fragment ion mass measurement to produce a large set of excellent Drosophila melanogaster
peptide identifications. This sort of data would normally receive a better rating than a single étoile. However, for some reason the investigators
choose to use urea as part of their experiment sample workup, leading to an observable amount of lysine carbamylation in
their proteins. The presence of these carbamylations (Lys + 43 Da) makes unambiguously determining acetylation (Lys +42 Da)
much more difficult than would have been necessary if a urea-free sample workup protocol had been utilized.
Data set of the week: (2011/10/23)
A phospho-proteomic screen identifies substrates of the checkpoint kinase Chk1. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 2 LC/MS/MS runs,
using a covalent phosphopeptide capture method.
The data was published by
Blasius M, Forment JV, Thakkar N, Wagner SA, Choudhary C, and Jackson SP in
BMC Syst Biol. 2011 5:68 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 2 LC/MS/MS runs,
using a covalent phosphopeptide capture method.
The data was published by
Blasius M, Forment JV, Thakkar N, Wagner SA, Choudhary C, and Jackson SP in
BMC Syst Biol. 2011 5:68 (PubMed).
Any one interested in targeted phosphopeptide analysis should look at this
data carefully. The methods used here generated identifications that were > 99% phosphopeptides, for
the very specific proteins of interest in the cell-cycle checkpoint kinase Chk1 system. Every aspect of
the measurements was done well, while collecting a very small number of spectra compared to other techniques.
Even though there are relatively few spectra, there were a surprising number that were either unique
or the best obtained for that particular sequence.
 We often get asked questions about how fast a particular protein identification job can get
done, or how the choice of computer influences the throughput that can be expected in
a data analysis system. In part to answer these questions (and just for something to do
on a Friday afternoon), we ran a practical test using X! Tandem to see what effect different processors had
on the rate of processing spectra for a mid-sized data set. We tested six 64-bit processors, which were installed
in various computers around the lab. The test conditions (a bare minimum search) were as follows:
We often get asked questions about how fast a particular protein identification job can get
done, or how the choice of computer influences the throughput that can be expected in
a data analysis system. In part to answer these questions (and just for something to do
on a Friday afternoon), we ran a practical test using X! Tandem to see what effect different processors had
on the rate of processing spectra for a mid-sized data set. We tested six 64-bit processors, which were installed
in various computers around the lab. The test conditions (a bare minimum search) were as follows:
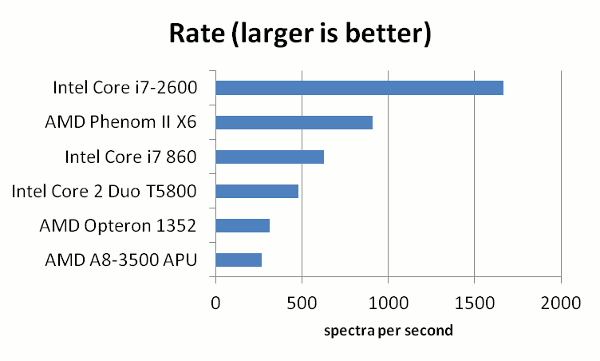
The results showed that there was a significant difference in the rate of processing spectra, depending
on the processor used. Predictably, the newest processors aimed at the gaming market (AMD Phenom X6 and the Intel i7-2600)
performed the best. The i7-2600 was clearly the winner, processing 1 spectrum every 600 microseconds. The following table
gives a few more details on the processors used.
 It is one thing to make a lot of information available, but it is something else to
get people to work with that information. We've put quite a bit of effort into making
GPM useful by trying to make the click-through experience consistent and the various
displays useful, original and intutitive. The chart below gives some guidance as to how intensively
people are using the GPM interface. The y-axis is the number of seconds a visitor uses the
site in a single session (as defined by Google Analytics) and the x-axis is the fraction
of visitor sessions that correspond to those time bins. Most users seem to visit the site for
3 to 5 minute sessions, with a significant number of people using the site for 30 minutes or more in a single session.
It is one thing to make a lot of information available, but it is something else to
get people to work with that information. We've put quite a bit of effort into making
GPM useful by trying to make the click-through experience consistent and the various
displays useful, original and intutitive. The chart below gives some guidance as to how intensively
people are using the GPM interface. The y-axis is the number of seconds a visitor uses the
site in a single session (as defined by Google Analytics) and the x-axis is the fraction
of visitor sessions that correspond to those time bins. Most users seem to visit the site for
3 to 5 minute sessions, with a significant number of people using the site for 30 minutes or more in a single session.
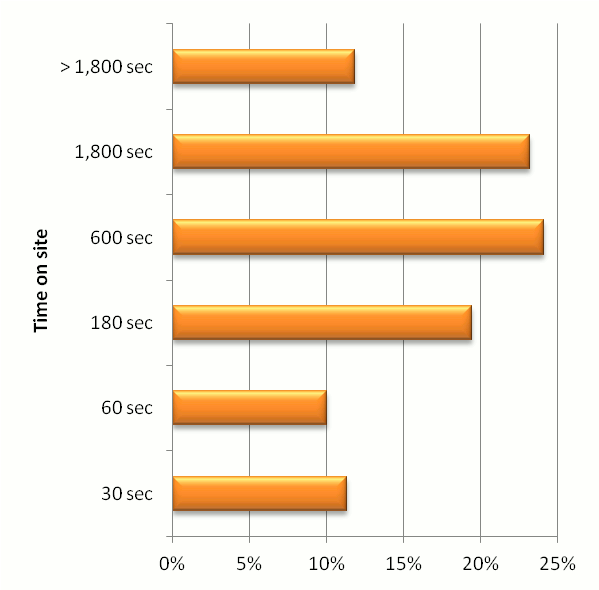
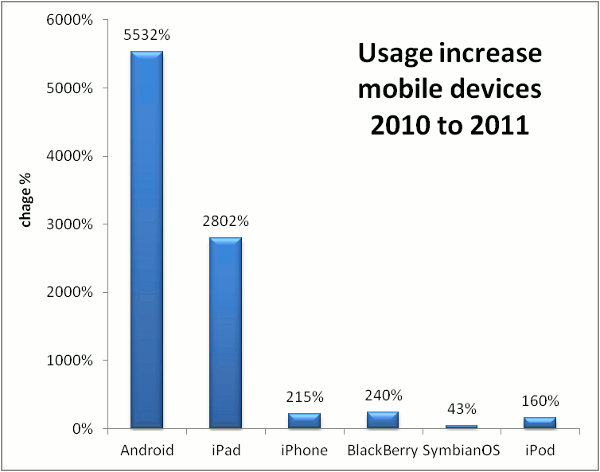
 Comparing the the use of GPMDB by scientists with different mobile devices, some clear trends have emerged.
The greatest increase in operating system use for accessing proteomics information
has been the Android OS, with a year-over-year growth rate of > 5,500%. Apple's
iPad operating system use has also grown very rapidly (2,800%), while most of the other
mobile operating systems have only shown modest growth. The differentiation between
these two and the others is most likely the size and resolution of the screens involved, but the
trends show that the older mobile operating systems (BlackBerry and Symbian) are not following the same
growth curve as the two leaders. The graph below shows the change in GPMDB usage by mobile device operating system,
comparing the one year period starting Oct 17, 2009 with the same period starting Oct. 17, 2010.
Comparing the the use of GPMDB by scientists with different mobile devices, some clear trends have emerged.
The greatest increase in operating system use for accessing proteomics information
has been the Android OS, with a year-over-year growth rate of > 5,500%. Apple's
iPad operating system use has also grown very rapidly (2,800%), while most of the other
mobile operating systems have only shown modest growth. The differentiation between
these two and the others is most likely the size and resolution of the screens involved, but the
trends show that the older mobile operating systems (BlackBerry and Symbian) are not following the same
growth curve as the two leaders. The graph below shows the change in GPMDB usage by mobile device operating system,
comparing the one year period starting Oct 17, 2009 with the same period starting Oct. 17, 2010.
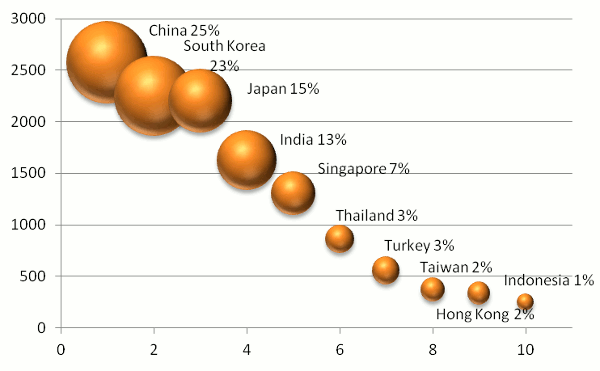
 China has become the leader in proteomics data reuse in Asia (25% of page views), with South Korea coming in a
very close second (at 23%). Beijing, Shanghai and Shenzhen were the leading cities in China, while Seoul, Incheon and
Gwangju were the leading cities in ROK. Japan (15%) and India (13%) placed third and fourth in Asia, overall. The bubble
chart below summarizes the results for the top ten Asian countries, where the size of the bubble indicates the fraction of
page views, the y-axis represents the number of user sessions and the x-axis indicates the country's numerical rank.
China has become the leader in proteomics data reuse in Asia (25% of page views), with South Korea coming in a
very close second (at 23%). Beijing, Shanghai and Shenzhen were the leading cities in China, while Seoul, Incheon and
Gwangju were the leading cities in ROK. Japan (15%) and India (13%) placed third and fourth in Asia, overall. The bubble
chart below summarizes the results for the top ten Asian countries, where the size of the bubble indicates the fraction of
page views, the y-axis represents the number of user sessions and the x-axis indicates the country's numerical rank.
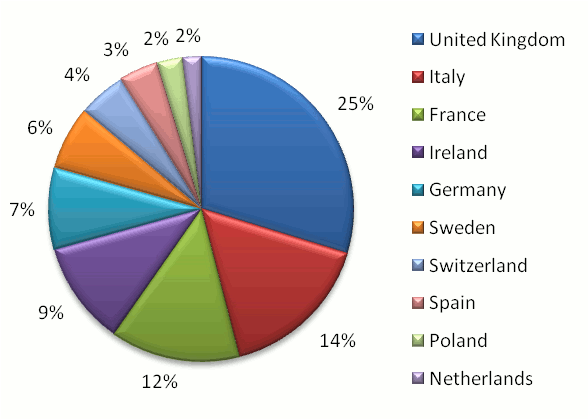
 The United Kingdom (consisting of England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland) has been a consistent leader in proteomics
data consumption and is the
top consumer of proteomics information in Europe with 25% of all European usage (according to GPMDB statistics). London,
Manchester, Cambridge, Liverpool & Newcastle upon Tyne were the five most active cities in England, Dundee and
Edinburgh in Scotland, Belfast in Northern Ireland and Cardiff in Wales.
Italy (14%) and France (12%) came in as the second and third place European countries overall. A chart representing the
relative proteomics data consumption rate of the top 10 European countries is shown below.
The United Kingdom (consisting of England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland) has been a consistent leader in proteomics
data consumption and is the
top consumer of proteomics information in Europe with 25% of all European usage (according to GPMDB statistics). London,
Manchester, Cambridge, Liverpool & Newcastle upon Tyne were the five most active cities in England, Dundee and
Edinburgh in Scotland, Belfast in Northern Ireland and Cardiff in Wales.
Italy (14%) and France (12%) came in as the second and third place European countries overall. A chart representing the
relative proteomics data consumption rate of the top 10 European countries is shown below.
 California has emerged as the state that is the clear leader in the use of proteomics information in the USA, with a surprising
31% of all USA pageviews (based
on our statistics for GPMDB). Of Californian cites, Duarte, Davis, Beverly Hills,
Los Angeles and La Jolla have been the consistent leaders. Washington (10%) and New York (9%) came in second and third place.
The lowest numbers of requests for information has been from Alaska and Wyoming, however all 50 states (and the District of Columbia)
have used GPMDB to some extent. The details of the
statistics for the top ten states are shown below.
California has emerged as the state that is the clear leader in the use of proteomics information in the USA, with a surprising
31% of all USA pageviews (based
on our statistics for GPMDB). Of Californian cites, Duarte, Davis, Beverly Hills,
Los Angeles and La Jolla have been the consistent leaders. Washington (10%) and New York (9%) came in second and third place.
The lowest numbers of requests for information has been from Alaska and Wyoming, however all 50 states (and the District of Columbia)
have used GPMDB to some extent. The details of the
statistics for the top ten states are shown below.
Data set of the week: (2011/10/16)
Global network analysis of drug tolerance, mode of action and virulence in methicillin-resistant S. aureus. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 10 LC/MS/MS runs,
using iTRAQ quantitation.
The data was published by
Overton IM, Graham S, Gould KA, Hinds J, Botting CH, Shirran S, Barton GJ, and Coote PJ in
BMC Syst Biol. 2011 5:68 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 10 LC/MS/MS runs,
using iTRAQ quantitation.
The data was published by
Overton IM, Graham S, Gould KA, Hinds J, Botting CH, Shirran S, Barton GJ, and Coote PJ in
BMC Syst Biol. 2011 5:68 (PubMed).
The data collected here was for a focussed study which was
well suited to analysis using a QQ-TOF style instrument and isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation.
Using the results the authors were able to draw some conclusions about changes in the concentrations
of the most abundant proteins in S. aureus, caused by their specific experimental conditions. The
protein concentration limit of detection was significantly higher than might be expected for
a survey-style proteomics study but in this case it was the perturbations in metabolic proteins
that was desired measurement, rather than a thorough catalogue of all proteins present.
Data set of the week: (2011/10/9)
DNA affects the composition of lipoplex protein corona: A proteomics approach. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 2 LC/MS/MS runs,
using label-free quantitation.
The data was published by
Capriotti AL, Caracciolo G, Caruso G, Foglia P, Pozzi D, Samperi R, and Laganà A in
Proteomics. 2011 11:3349-58 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 2 LC/MS/MS runs,
using label-free quantitation.
The data was published by
Capriotti AL, Caracciolo G, Caruso G, Foglia P, Pozzi D, Samperi R, and Laganà A in
Proteomics. 2011 11:3349-58 (PubMed).
This data was a nice demonstration of the use of protein isolation
methods to generate a much-reduced set of proteins (compared to blood plasma) associated with
a very specific biomedically-relevant stimulus. The identifications were sound and the
overall experimental setup produced a good set of appropriate peptides for the
proteins found in this study, all of which are well-known plasma proteins.
A hardware failure has shut down the GPM's FTP site for the next few days,
until we can get replacement equipment and put it on-line.
 The proteomes for human and mouse have been updated to ENSEMBL v. 64, which was released late last week.
The human sequences are based on the most recent patch of the Genome Reference Consortium's human genome
sequence, GRCh37 Patch Release 5.
The snAP information information for both species has also been updated, corresponding to human dbSNP 132 & ENSEMBL (human) and
dbSNP 128 (mouse). The spectrum libraries and proteotypic peptide lists have also been updated for these
two species.
The proteomes for human and mouse have been updated to ENSEMBL v. 64, which was released late last week.
The human sequences are based on the most recent patch of the Genome Reference Consortium's human genome
sequence, GRCh37 Patch Release 5.
The snAP information information for both species has also been updated, corresponding to human dbSNP 132 & ENSEMBL (human) and
dbSNP 128 (mouse). The spectrum libraries and proteotypic peptide lists have also been updated for these
two species.
Data set of the week: (2011/09/18)
Shotgun proteomic analysis of the unicellular alga Ostreococcus tauri. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 235 result sets,
corresponding to normal peptides, phosphopeptides and 15N labelled SILAC experiments.
The data was published by
Le Bihan T, Martin SF, Chirnside ES, van Ooijen G, Barrios-Llerena ME, O'Neill JS, Shliaha PV, Kerr LE, and Millar AJ. in
J Proteomics. 2011 74:2060-70 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 235 result sets,
corresponding to normal peptides, phosphopeptides and 15N labelled SILAC experiments.
The data was published by
Le Bihan T, Martin SF, Chirnside ES, van Ooijen G, Barrios-Llerena ME, O'Neill JS, Shliaha PV, Kerr LE, and Millar AJ. in
J Proteomics. 2011 74:2060-70 (PubMed).
This paper does an excellent job of characterizing the proteome of a very unusual
eukaryote, Ostreococcus tauri.
Discovered in 1994, it is still the smallest known eukaryote in size — at 0.8 microns in diameter, 1000 O. tauri
cells would fit in a HeLa cell, with plenty of room left over. This data set thoroughly examines the proteome
of the organism, which has significant sequence divergence from the model eukaryotes commonly used in proteomics experiments. Any group interested in
the molecular evolution of phosphorylation signalling should find their phosphopeptide isolations instructive.
This data holds the modern record for the shear volume of tryptic peptide sequences that had never been observed before these spectra became publicly available.
The methods used here should serve as a guide for anyone interested in characterizing the proteome of a novel, single-celled eukaryote.
Data set of the week: (2011/09/11)
Quantitative phospho-proteomics to investigate the Polo-like kinase 1-dependent phospho-proteome. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 27 LC/MS/MS runs,
each corresponding to an SCX fraction from an IMAC enrichment of acidic peptides.
The data was published by
Grosstessner-Hain K, Hegemann B, Novatchkova M, Rameseder J, Joughin BA, Hudecz O, Roitinger E, Pichler P, Kraut N, Yaffe MB, Peters JM, and Mechtler K. in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 Aug 21 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 27 LC/MS/MS runs,
each corresponding to an SCX fraction from an IMAC enrichment of acidic peptides.
The data was published by
Grosstessner-Hain K, Hegemann B, Novatchkova M, Rameseder J, Joughin BA, Hudecz O, Roitinger E, Pichler P, Kraut N, Yaffe MB, Peters JM, and Mechtler K. in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 Aug 21 (PubMed).
What separated this study from other surveys of HeLa cell phosphopeptides was the
use of a SILAC approach that has significant benefits. Rather than relying on
metabolic incorporation of heavy amino acids, this study used light and heavy methyl groups, added to
the acidic groups of the cleaved peptides (Glu, Asp and C-terminus). This treatment
blocked all of the acidic groups in these peptides, except for the phosphorylated Ser, Thr and Tyr residues.
Because of this protocol, the
IMAC enrichment produced an unusually pure set of phosphopeptides that were not dominated by peptides
containing additional acidic side chains, as is often the case with IMAC experiments. It also
generated particularly simple, accurate peptide quantitation.
Data set of the week: (2011/09/04)
Proteomic analysis of outer membrane vesicles derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 4 groups of spectra,
one large scale survey run and three small separate analyses.
The data was published by
Choi DS, Kim DK, Choi SJ, Lee J, Choi JP, Rho S, Park SH, Kim YK, Hwang D, Gho YS. in
Proteomics 2011 11:3424-9 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 4 groups of spectra,
one large scale survey run and three small separate analyses.
The data was published by
Choi DS, Kim DK, Choi SJ, Lee J, Choi JP, Rho S, Park SH, Kim YK, Hwang D, Gho YS. in
Proteomics 2011 11:3424-9 (PubMed).
The data reported here gives a first look at the outer membrane proteins
of this important pathogenic species. The proteins discovered and the techniques used provide
an excellent comparison with the proteins found for the related species, Pseudomonas syringae, in
a previously featured data set. The results would have been more
broadly applicable at the peptide level if the chromatography had been better, but the proteins
identified were based on very good ion-trap spectra and the data analysis used
in the manuscript was appropriate.
 The US National Cancer Institute has issued a new round of Requests for Application, based on a set
of questions generated by a series of workshops and on-line submissions. These "Provocative
Questions" and the associated RFAs can be found on the NCI web site here.
From the NCI web site, explaining the rationale for this new process: The US National Cancer Institute has issued a new round of Requests for Application, based on a set
of questions generated by a series of workshops and on-line submissions. These "Provocative
Questions" and the associated RFAs can be found on the NCI web site here.
From the NCI web site, explaining the rationale for this new process:
The collaborative process of formulating the provocative questions
should engage the NCI’s scientific community in serious debate and energize the NCI’s many constituencies
(advocacy groups, health professionals, Members of Congress, and others) about the prospects for improving
the welfare of cancer patients through research. These other constituencies are encouraged to take part in
the "Provocative Questions" enterprise through discussions and activities ...
Data set of the week: (2011/08/29)
A tissue-specific atlas of mouse protein phosphorylation and expression. Overall rating: 
 This data set was made available in TRANCHE as 312 LC/MS/MS
runs using metal oxide affinity to enrich fractions with phosphopeptides from mouse tissue samples.
The data was published by
Huttlin EL, Jedrychowski MP, Elias JE, Goswami T, Rad R, Beausoleil SA, Villén J, Haas W, Sowa ME, and Gygi SP. in
Cell. 2010 143:1174-89 (PubMed).
This data set was made available in TRANCHE as 312 LC/MS/MS
runs using metal oxide affinity to enrich fractions with phosphopeptides from mouse tissue samples.
The data was published by
Huttlin EL, Jedrychowski MP, Elias JE, Goswami T, Rad R, Beausoleil SA, Villén J, Haas W, Sowa ME, and Gygi SP. in
Cell. 2010 143:1174-89 (PubMed).
The data gives a general survey of the most abundant phosphopeptides that
were found in nine different mouse tissue samples. The phosphopeptide enrichment was lower than
in other, more specific studies and the chromatography was somewhat less consistently performed than
has become best-practice in the field. The study did, however, provide many good observations of phosphorylation
sites in proteins that are not well-represented in cell culture studies.
 The final version of the
scientific and social programme for the Human Proteome Organization's 2011 World Congress in Geneva, Switzerland
has been made available (click here for a PDF
version). The meeting is a combination of the HUPO 10th Annual World Congress,
the 5th EuPA Annual Scientific Meeting and the 8th SPS scientific meeting and will run from September 4-7, 2011.
This year's Congress has placed special emphasis on translational research, as well as the
usual sessions associated with HUPO initiatives, methods and instrumental developments. The final version of the
scientific and social programme for the Human Proteome Organization's 2011 World Congress in Geneva, Switzerland
has been made available (click here for a PDF
version). The meeting is a combination of the HUPO 10th Annual World Congress,
the 5th EuPA Annual Scientific Meeting and the 8th SPS scientific meeting and will run from September 4-7, 2011.
This year's Congress has placed special emphasis on translational research, as well as the
usual sessions associated with HUPO initiatives, methods and instrumental developments.
 The US National Cancer Institute
has announced the successful applicants for its next round of proteomics centers for cancer research (Clinical Proteomic Technologies for Cancer, CPTAC).
These centers are dispersed around the US and many of them have more than one geographical location. The
titles for the Centers and their institutional affiliations are given below — from information posted on
the NIH project web site: The US National Cancer Institute
has announced the successful applicants for its next round of proteomics centers for cancer research (Clinical Proteomic Technologies for Cancer, CPTAC).
These centers are dispersed around the US and many of them have more than one geographical location. The
titles for the Centers and their institutional affiliations are given below — from information posted on
the NIH project web site:
Data set of the week: (2011/08/21)
Quantitative phosphoproteomics identifies substrates and functional modules of Aurora and Polo-like kinase activities in mitotic cells. Overall rating: 
 This data set was made available in TRANCHE as 100 LC/MS/MS
runs that use a combination of SILAC and metal oxide affinity purification methods.
The data was published by
Kettenbach AN, Schweppe DK, Faherty BK, Pechenick D, Pletnev AA, and Gerber SA in
Sci Signal. 2011 Jun 28, 4(179):rs5 (PubMed).
This data set was made available in TRANCHE as 100 LC/MS/MS
runs that use a combination of SILAC and metal oxide affinity purification methods.
The data was published by
Kettenbach AN, Schweppe DK, Faherty BK, Pechenick D, Pletnev AA, and Gerber SA in
Sci Signal. 2011 Jun 28, 4(179):rs5 (PubMed).
This paper provides a good survey of the phosphopeptides present in HeLa cells and
should be viewed as a model for further study of quantitative phophoproteomics in cell culture. The
experimental analysis used CID fragmentation and it demonstrates very clearly that it is not
necessary (or desirable) to use ETD when looking for sensitive, reproducible phosphopeptide
quantitation. The data analysis in the paper has some flaws, but the conclusions were reasonable and within
the limitations of the analytical approach that was used.
 The NIH has made available a strategy document outlining its potential directions in funding the
development of new proteomics technology, entitled: Disruptive Proteomics Technologies: Comprehensive Protein Identification in Clinical Samples.
This document describes at least two separate tracks of Funding Opportunity Announcements (FOAs) that
would potentially be open to researchers. These ideas were part of an Innovation Brainstorm and it is unclear
from the current information on the Web whether they will result in real programs. The potential areas
of funding were as follows (from the NIH Common Funds site):
The NIH has made available a strategy document outlining its potential directions in funding the
development of new proteomics technology, entitled: Disruptive Proteomics Technologies: Comprehensive Protein Identification in Clinical Samples.
This document describes at least two separate tracks of Funding Opportunity Announcements (FOAs) that
would potentially be open to researchers. These ideas were part of an Innovation Brainstorm and it is unclear
from the current information on the Web whether they will result in real programs. The potential areas
of funding were as follows (from the NIH Common Funds site):
FOA 1: Technology Development: MS-based protein ID and quantitation . (Years 1-5)
Goals include:
FOA 2: Technology Development: Non-MS-based protein ID and quantitation.
Goals include:
Data set of the week: (2011/08/14)
Proteome profiling of wild type and lumican-deficient mouse corneas. Overall rating: 
 This data set was made available as 48 LC/MS/MS
runs from a series of MudPit experiments.
The data was published by
Shao H, Chaerkady R, Chen S, Pinto SM, Sharma R, Delanghe B, Birk DE, Pandey A, and Chakravarti S in
J Proteomics. 2011 May 17 (PubMed).
This data set was made available as 48 LC/MS/MS
runs from a series of MudPit experiments.
The data was published by
Shao H, Chaerkady R, Chen S, Pinto SM, Sharma R, Delanghe B, Birk DE, Pandey A, and Chakravarti S in
J Proteomics. 2011 May 17 (PubMed).
These experiments truly answered the question: "What proteins are present in
mouse corneas?" It contains excellent observations of many not-so-common collagens, keratins and a variety of other
proteins associated with intermediate filaments, such as desmoplakin, periplakin, envoplakin and
uroplakin. The original data analysis presented in the paper was very deeply flawed: it should not
be considered reliable. The data itself, though, was an excellent example of the benefits of using an
Orbitrap-LTQ hybrid instrument with a sensitive HCD collision cell.
Data set of the week: (2011/08/08)
Proteomic analysis of microvesicles derived from human colorectal cancer ascites. Overall rating: 
 This data set was made available as 3 summary sets
created from a combination of 1-D SDS-PAGE gel bands and LC/MS/MS runs.
The data was published by
Choi DS, Park JO, Jang SC, Yoon YJ, Jung JW, Choi DY, Kim JW, Kang JS, Park J, Hwang D, Lee KH, Park SH, Kim YK, Desiderio DM, Kim KP, and Gho YS in
Proteomics 2011 11:2745-51 (PubMed).
This data set was made available as 3 summary sets
created from a combination of 1-D SDS-PAGE gel bands and LC/MS/MS runs.
The data was published by
Choi DS, Park JO, Jang SC, Yoon YJ, Jung JW, Choi DY, Kim JW, Kang JS, Park J, Hwang D, Lee KH, Park SH, Kim YK, Desiderio DM, Kim KP, and Gho YS in
Proteomics 2011 11:2745-51 (PubMed).
The experiments performed here provide about as much information as can be obtained
from a clinically obtained sample — in this case ascities from human colorectal cancer patients — using gel band analysis and
an LTQ mass spectrometer. The identifications were good quality and they provide a good template for the proteins
to be expected in the micro-vesicular fraction of this class of clinical isolates. The results were
relatively free of artifacts and comparision of the three isolates provides an interesting example of the
variability that can be expected from real samples related only by their method of isolation.
For anyone interested, these three result sets can be used to compare the utility of
a purely web-based system (GPMDB) with a local client computer app (PRIDE's new PRIDE Inspector utility). To use
PRIDE Inspector, click on the "PRIDE" link for any of the three data sets and then click on the
red "PRIDE Inspector" link on the resulting page. You will need to have Java installed on your computer
(this will not work on most smart phones or iPad tablets).
 It hardly seems like a year has passed, but one year ago we released the first version of the
GPMDB Guide to the Human Proteome. We are happy to be releasing the 2011.08.01 edition,
which adds many new proteins to the Guide. The new Guide is based on almost twice as much data as the
original, because of the large increase in data submitted to the GPMDB. At the same time, we are
releasing the Guide to the Mouse Proteome, version 2011.08.01.
These guides will be released on a quarterly basis from this date forward.
It hardly seems like a year has passed, but one year ago we released the first version of the
GPMDB Guide to the Human Proteome. We are happy to be releasing the 2011.08.01 edition,
which adds many new proteins to the Guide. The new Guide is based on almost twice as much data as the
original, because of the large increase in data submitted to the GPMDB. At the same time, we are
releasing the Guide to the Mouse Proteome, version 2011.08.01.
These guides will be released on a quarterly basis from this date forward.
 The European Proteomics Association (EuPA) has released its July 2011 Bulletin
(click here to download).
From their web site:
The European Proteomics Association (EuPA) has released its July 2011 Bulletin
(click here to download).
From their web site:
The 5th issue of the EuPA bulletin has been released. It contains this month the message from the president
and EuPA latest news, information from the Italian and Turkish proteomics societies, meeting reports,
plant proteomics initiatives reports,
information from the Journal of Proteomics, and many other information from the proteomics world.
Data set of the week: (2011/07/31)
Global profiling of proteolysis during rupture of Plasmodium falciparum from the host erythrocyte. Overall rating: 
 This data set was made available as 760 gel band
identifications, where each GPM model is the analysis of an individual gel band.
The data was published by
Bowyer PW, Simon GM, Cravatt BF, and Bogyo M. in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011, 10:M110.001636 (PubMed).
This data set was made available as 760 gel band
identifications, where each GPM model is the analysis of an individual gel band.
The data was published by
Bowyer PW, Simon GM, Cravatt BF, and Bogyo M. in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011, 10:M110.001636 (PubMed).
This study generated a large number of gel bands from a critical point in the life cycle
of the protozoan parasite Plasmodium
falciparum in the context of its normal home for the part of its life cycle as the causitive
agent of malaria, the human erythrocyte. The results provide insights into the organism's metabolism as
it exists as a schizont containing multiple merozoites (inside of a erythrocyte) and the subsequent rupturing of
the infected erythrocyte. The data provides an excellent example of the bioinformatics challenges associated with
the analysis of multi-proteome samples, even when they are nicely isolated into gel bands and the
proteomes have little sequence overlap.
Data set of the week: (2011/07/24)
in vivo versus in vitro protein abundance analysis of Shigella dysenteriae type 1 reveals changes in the expression of proteins involved in virulence, stress and energy metabolism. Overall rating: 
 This data set was made available as 19 MudPIT
experiments, where each GPM model is a summary of all the individual LC/MS/MS runs.
The data was published by
Kuntumalla S, Zhang Q, Braisted JC, Fleischmann RD, Peterson SN, Donohue-Rolfe A, Tzipori S, and Pieper R in
BMC Microbiol. 2011 11:147 (PubMed).
This data set was made available as 19 MudPIT
experiments, where each GPM model is a summary of all the individual LC/MS/MS runs.
The data was published by
Kuntumalla S, Zhang Q, Braisted JC, Fleischmann RD, Peterson SN, Donohue-Rolfe A, Tzipori S, and Pieper R in
BMC Microbiol. 2011 11:147 (PubMed).
These experiments provided the most comprehensive collection of peptide identifications
for the important pathogenic enterobacteria species Shigella dysenteriae,
a close relative of the common Escherichia coli. Type 1 S. dysenteriae causes a severe form of dysentery
referred to as shigellosis. The experiments reported here use whole cell lysates to try to understand protein
abundances using label-free methods. The proteins found showed significant cleavage at non-tryptic sites (up to 10% of identified peptides), probably
caused by endogenous proteases in the lysate itself rather simple chymotryptic activity in the cleavage reagent used.
The peptide identifications also revealed extensive deamidation of both Q and N residues.
 The ProteomeXchange group has released the draft documents corresponding to its Workpackage 4.1 deliverables in PDF format.
These documents are in fulfillment of the ProteomeXchange group's commitment to release these
workpackage deliverables to the public, through their web
site. The specific deliverables that have been made available are as follows:
The ProteomeXchange group has released the draft documents corresponding to its Workpackage 4.1 deliverables in PDF format.
These documents are in fulfillment of the ProteomeXchange group's commitment to release these
workpackage deliverables to the public, through their web
site. The specific deliverables that have been made available are as follows:D4.1 - ProteomeXchange repository data flow definition, and D4.2 - ProteomeXchange metadata format definition.
D4.1 describes the overall vision of the central role of PRIDE in archiving and maintaining the tables of
identifications produced for publications in addition to their established role of generating new XML formats to set these tables in context.
D4.2 describes the first of these new XMLs — ProteomeXchangeDataset. This new XML will be used to describe data
submissions to PRIDE (in a very similar way to the existing PRIDE submission XML), but with new field
names and some new fields for additional ontology information. As well, there will be provision for an overall accession number to be
generated by the new EBI entity ProteomeCentral, which has a tentative launch date of Dec. 31, 2012. Links to
files coded in this new XML will be made available via another XML, the RDF Site Summary (RSS).
RSS feeds are commonly used by information providers to list updates to a web site. If you are unfamiliar with RSS
feeds, try the existing
feeds for PRIDE, Tranche and
GPMDB's Protein-of-the-day to see
what sort of information they can make available.
GPMDB adopts the Human Genome Variation Society conventions for amino acid polymorphisms (2011/07/19)
 GPMDB has been collecting information about single amino acid polymorphisms (sAPs) since it
began. For the last four years, we have routinely been tracking sAPs caused by known SNPs (which we refer to as snAPs). This
tracking has mainly
utilized the RefSNP numbering system ("rs" numbers) to track the known SNPs associated with specific amino acid polymorphisms. As
our collection of amino acid polymorphism information has grown and we have begun to track this type
of information for an increasing number of species, this older nucleic acid based system has become unwieldy for
general use.
GPMDB has been collecting information about single amino acid polymorphisms (sAPs) since it
began. For the last four years, we have routinely been tracking sAPs caused by known SNPs (which we refer to as snAPs). This
tracking has mainly
utilized the RefSNP numbering system ("rs" numbers) to track the known SNPs associated with specific amino acid polymorphisms. As
our collection of amino acid polymorphism information has grown and we have begun to track this type
of information for an increasing number of species, this older nucleic acid based system has become unwieldy for
general use.
We will maintain the use of the RefSNP to track the origins of snAPs, but to serve our wider needs for a protein splice
specific method of tracking sAPs in general, we have adopted the
Human Genome Variation Society
nomenclature recommendations for protein
sAPs. This system is fairly simply and it is readily mapped onto any set of protein accession numbers that a
user might like to use. For example, the snAP corresponding to the SNP "rs30855079" can now be accessed using
the HGVS-style nomenclature:
ENSMUSP00000107760:p.I541V, or ENSMUSP00000107760:p.Ile541Val where "ENSMUSP00000107760" is the accesssion number for the protein (mouse Pzp) and "I541V" is the original residue (I), its position in the protein (residue #541) and the mutated residue (V). If the identify of either residue is unknown, either "X" or "Xxx" may be substituted as a wild-card place holder. A specific snAP in this format can be accessed either by entering that value into the GPMDB SNAP interface or directly as a URL using the convention: http://gpmdb.thegpm.org/protein/snap/ENSMUSP00000107760:p.I541V The accession number can be any that have been used by the GPM, such as yeast "Y" ORF numbers. NCBI gi numbers and SwissProt accessions require their normalized formats "gi|...|" and "sp|...|", respectively. Data set of the week: (2011/07/17)
Glycoprotein capture and quantitative phosphoproteomics indicate coordinated regulation of cell migration upon lysophosphatidic acid stimulation. Overall rating: 
 This data set was made available as 70 LC/MS/MS
runs, corresonding to various affinity purification and quantitation schemes.
The data was published by
Mäusbacher N, Schreiber TB, and Daub H. in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010 9:2337-53 (PubMed).
This data set was made available as 70 LC/MS/MS
runs, corresonding to various affinity purification and quantitation schemes.
The data was published by
Mäusbacher N, Schreiber TB, and Daub H. in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010 9:2337-53 (PubMed).
These experiments demonstrate the value of using a multiple-step affinity purification
strategy to investigate molecules of interest. Here the authors use a combination of lectins to capture glycoproteins and
titanium oxide to capture highly acidic peptides. These peptides allowed them to investigate cell surface protein responses to lysophosphatidic acid
treatment. The set of peptides captured were quite different from a typical metal-oxide pulldown experiment,
as the intracellular proteins with large numbers of high occupancy phopho-domains that tend to dominate the results
were mainly absent (such as the usual suspects SRRM2, P53BP1, TRIM28, MAP1A, NPM, et fratres eorum). These high abundance phosphoproteins
do not have the necessary glycosylation to have been pulled-down in the first step and therefore they were almost completely removed. This simple
purification procedure allowed the reliable detection and quantitation of relatively low occupancy phospho-domains, such as those in WNK1,
PTPRK and DTX3L.
 ORCID, the Open Researcher & Contributor ID Initiative, will
be holding a workshop in Helsinki, Finland on Sept. 12–13, 2011 (workshop
website). The purpose of the conference (and ORCID) is to come up with an agreed upon global method
of unambiguously identifying authors in scientific communications. Simply using people's names causes all sorts
of problems and confusion for people trying to organize databases of scientific literature, results or data. The goals
of this workshop are as follows (taken from the IRISC website):
ORCID, the Open Researcher & Contributor ID Initiative, will
be holding a workshop in Helsinki, Finland on Sept. 12–13, 2011 (workshop
website). The purpose of the conference (and ORCID) is to come up with an agreed upon global method
of unambiguously identifying authors in scientific communications. Simply using people's names causes all sorts
of problems and confusion for people trying to organize databases of scientific literature, results or data. The goals
of this workshop are as follows (taken from the IRISC website):
 PRIME-XS, a European Union Framework project, as been funded
to a level of US$11.5 million. The
purpose of PRIME-XS is to provide access to state-of-the art instrumentation to research projects
within the European Union. They are now accepting proposals for projects to utilize the infrastructure. From their web site:
PRIME-XS, a European Union Framework project, as been funded
to a level of US$11.5 million. The
purpose of PRIME-XS is to provide access to state-of-the art instrumentation to research projects
within the European Union. They are now accepting proposals for projects to utilize the infrastructure. From their web site:Starting today, July 5th 2011, researchers in all EU member states and associated countries can submit a project proposal via the online application system of PRIME-XS. European researchers can request access to proteomics techniques at the six access facilities of PRIME-XS via an online application. Researchers can choose a preferential access facility where the project should be carried out and propose the proteomics technology they would like to use. All project proposals will be peer reviewed by independent reviewers. If the application is positively evaluated, the researcher is allowed to perform the experiment at the access facility. The users can get practical support with final sample preparation and staff of PRIME-XS will perform the proteomics data acquisition. Users will be able to visit the access facility, gain experience on sample preparation, sample analysis and data handling and analysis.  The European Bioinformatics Institute's proteomics database PRIDE will be operating
with limited service from July 8 to July 13 because of maintenance. From the PRIDE
web site:
The European Bioinformatics Institute's proteomics database PRIDE will be operating
with limited service from July 8 to July 13 because of maintenance. From the PRIDE
web site:PRIDE is currently undergoing unplanned but necessary database maintenance and normal service should resume by Wednesday, July 13. . This means that no new submissions are going to be processed until that time and users are encouraged not to create new user accounts as there might be some disruptions during this time. Thank you for your understanding. Data set of the week: (2011/07/10)
A high-quality catalog of the Drosophila melanogaster proteome. Overall rating: 
 This data set was made available as 1,907 LC/MS/MS
runs, through the PeptideAtlas data repository.
The data was published by
Brunner E, Ahrens CH, Mohanty S, Baetschmann H, Loevenich S, Potthast F, Deutsch EW, Panse C, de Lichtenberg U,
Rinner O, Lee H, Pedrioli PG, Malmstrom J, Koehler K,
Schrimpf S, Krijgsveld J, Kregenow F, Heck AJ, Hafen E, Schlapbach R, and Aebersold R. in
Nat Biotechnol. 2007, 25:576-83 (PubMed).
This data set was made available as 1,907 LC/MS/MS
runs, through the PeptideAtlas data repository.
The data was published by
Brunner E, Ahrens CH, Mohanty S, Baetschmann H, Loevenich S, Potthast F, Deutsch EW, Panse C, de Lichtenberg U,
Rinner O, Lee H, Pedrioli PG, Malmstrom J, Koehler K,
Schrimpf S, Krijgsveld J, Kregenow F, Heck AJ, Hafen E, Schlapbach R, and Aebersold R. in
Nat Biotechnol. 2007, 25:576-83 (PubMed).
The work was one of the best of the once popular attempts to create a full-body proteome atlas of
an organism. In this case a model organism of historical interest, the fruit fly, was used and a large number
of Thermo LTQ and LCQ Classic runs were recorded. While an achievement at the
time (only 5 years ago), the relatively small number of identifications obtained per run and the very small amount of
quantitative information available makes this study seem a little dated. However, it still provides quite
a bit of insight about the most abundant proteins present in D. melanogaster and a general overview of those proteins' relative
concentration in a variety of organs and developmental stages, such as
larvae,
pupa membranes,
adult heads,
adult membranes,
adult membranes, and
adult brains.
 GPM offers the choice of searching with UniProt sequences in the boutique servers for
Homo sapiens, Mus musculus and Rattus norvegicus. Recently, UniProt
has started to make available speciality collections for the species that used to
be covered by the now-defunct International Protein Index (IPI). We have updated our UniProt
sequences for those species to use the most recent version of these new IPI-replacements, as
well as adding the metadata associated with the UniProt builds into the sequence list
files, as has been standard for the NCBI- and ENSEMBL-sourced sequences for some time.
GPM offers the choice of searching with UniProt sequences in the boutique servers for
Homo sapiens, Mus musculus and Rattus norvegicus. Recently, UniProt
has started to make available speciality collections for the species that used to
be covered by the now-defunct International Protein Index (IPI). We have updated our UniProt
sequences for those species to use the most recent version of these new IPI-replacements, as
well as adding the metadata associated with the UniProt builds into the sequence list
files, as has been standard for the NCBI- and ENSEMBL-sourced sequences for some time.
Data set of the week: (2011/07/04)
A cost-benefit analysis of multidimensional fractionation of affinity purification-mass spectrometry samples. Overall rating: 
 This data set was made available as 105 LC/MS/MS runs,
organized by the specific experimental techniques used.
The data was published by
Dunham WH, Larsen B, Tate S, Badillo BG, Goudreault M, Tehami Y, Kislinger T, and Gingras AC in
Proteomics. 2011, 11:2603-12 (PubMed).
This data set was made available as 105 LC/MS/MS runs,
organized by the specific experimental techniques used.
The data was published by
Dunham WH, Larsen B, Tate S, Badillo BG, Goudreault M, Tehami Y, Kislinger T, and Gingras AC in
Proteomics. 2011, 11:2603-12 (PubMed).
These experiments were performed to provide a systematic evaluation of the use
of several common sample preparation/separation techniques for the analysis of the type of affinity purified samples
commonly used to determine protein-protein interaction partners. In this type of experiment the total number of proteins
identified has to be carefully balanced against the background level proteins present due to non-specific protein interactions.
The authors do a careful job of applying common methods and studying the results provides a number of interesting
case studies that can be used in both planning experiments and teaching practitioners (even experienced ones) about the
intricacies of this important class of samples.
Data set of the week: (2011/06/27)
Accurate quantification of more than 4000 mouse tissue proteins reveals minimal proteome changes during aging. Overall rating: 
 This data set was made available as 119 data files,
organized by the tissue sampled.
The data was published by
Walther DM, and Mann M. in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 10:M110.004523 (PubMed).
This data set was made available as 119 data files,
organized by the tissue sampled.
The data was published by
Walther DM, and Mann M. in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 10:M110.004523 (PubMed).
This study is a large, multiple tissue examination of the effects of aging on
the proteome of M. musculus. The results give a very good survey of the distributions of proteins
that can be studied by whole mouse SILAC in a set of tissues: heart, kidney, cerebellum, frontal cortex, and hippocampus. The
interesting finding of the study was that there was little quantitative change in the proteins found:
aging seems to be a more subtle effect than can be accounted for by gross changes in a tissue's proteome composition.
 We are experimenting with ways to use the self-contained relational database engine
SQLite. This system allows you to
create and use an SQL-queryable database contained in a single file. Our first
attempt to use this approach is to create a GPMDB database schema
that is both compatible with SQLite and conforms to the pattern of queries that can
be performed on a full GPMDB installation. This new schema is meant to record
the results of a single identification run: it corresponds to the identifications in a single
GPM XML result file.
We are experimenting with ways to use the self-contained relational database engine
SQLite. This system allows you to
create and use an SQL-queryable database contained in a single file. Our first
attempt to use this approach is to create a GPMDB database schema
that is both compatible with SQLite and conforms to the pattern of queries that can
be performed on a full GPMDB installation. This new schema is meant to record
the results of a single identification run: it corresponds to the identifications in a single
GPM XML result file.
A new link has been added to the main model display in GPM to allow users to generate
their own GPMDB-SQLite database for any GPM result online. Simply click the "sqlite" link on
a model page you are interested in (the link position is illustrated
below) and you will be taken to a page that will track the generation of the associated
".gpmdb" database file. It takes some time to create the new database, so please be patient.

 The first Cascadia Proteomics Symposium will be held July 17th—July 19th, 2011, at the
Institute for Systems Biology in Seattle Washington (see cascadiaproteomics.org
for details). From the conference informational flyer: The Cascadia Proteomics Symposium is a new regional conference
that aims to bring together the large number of proteomics researchers in Washington, Oregon, and British Columbia
to discuss our research, get to know each other better, share ideas and foster collaboration within this region.
We are putting specific emphasis on organizing a conference with a very low attendance cost to encourage as many
members of each lab to participate as possible,
including those that may not normally be able to attend the usual national and global conferences.
The first Cascadia Proteomics Symposium will be held July 17th—July 19th, 2011, at the
Institute for Systems Biology in Seattle Washington (see cascadiaproteomics.org
for details). From the conference informational flyer: The Cascadia Proteomics Symposium is a new regional conference
that aims to bring together the large number of proteomics researchers in Washington, Oregon, and British Columbia
to discuss our research, get to know each other better, share ideas and foster collaboration within this region.
We are putting specific emphasis on organizing a conference with a very low attendance cost to encourage as many
members of each lab to participate as possible,
including those that may not normally be able to attend the usual national and global conferences.
 June 23rd is the deadline for submission of "Late-Breaking Abstracts" for
HUPO 2011 in Geneva. Also on the 23rd,
La Société Française d'Electrophorèse et d'Analyse Protéomique will be holding its
Colloque inaugural
Human Proteome Project - France in Paris to discuss the merits of focussing on human chromosomes 2 and 14. The SFEAP host a rather
nice calendar of upcoming proteomics events, which is worth checking out
if you are interested in European proteomics meetings. Registration
is also open for the British Society for Proteome Research's BSPR-EBI 8th
annual meeting in Cambridge, UK (final programme).
June 23rd is the deadline for submission of "Late-Breaking Abstracts" for
HUPO 2011 in Geneva. Also on the 23rd,
La Société Française d'Electrophorèse et d'Analyse Protéomique will be holding its
Colloque inaugural
Human Proteome Project - France in Paris to discuss the merits of focussing on human chromosomes 2 and 14. The SFEAP host a rather
nice calendar of upcoming proteomics events, which is worth checking out
if you are interested in European proteomics meetings. Registration
is also open for the British Society for Proteome Research's BSPR-EBI 8th
annual meeting in Cambridge, UK (final programme).
Data set of the week: (2011/06/19)
Large scale phosphoproteome profiles comprehensive features of mouse embryonic stem cells. Overall rating: 
 This data set was made available as 12 large experiments.
The data was published by
Li QR, Xing XB, Chen TT, Li RX, Dai J, Sheng QH, Xin SM, Zhu LL, Jin Y, Pei G, Kang JH, Li YX, and Zeng R. in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 10:M110.001750 (PubMed).
This data set was made available as 12 large experiments.
The data was published by
Li QR, Xing XB, Chen TT, Li RX, Dai J, Sheng QH, Xin SM, Zhu LL, Jin Y, Pei G, Kang JH, Li YX, and Zeng R. in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 10:M110.001750 (PubMed).
When the authors referred to their study as "Large scale", they were not kidding.
The data made available rather thoroughly captures the proteins and peptides that can be observed
using current technology from whole cell lysates of mouse embryonic stem cells. The identifications were
very high quality and the chromatography was consistent. The only small flaw was the trypsin used: it
cleaved bonds between K-P, R-P and H-X more frequently than one might hope in a study of this sort. It is not
uncommon that trypsin will cleave these non-cannonical sites, but the frequency of this type of cleavage in this study
was unusually high.
This is possibly the first use of a protein sequence to generate music. It was
developed by the SMART (Science Meets ART) collective,
and in their words: [to] use music to describe the complexity of biomolecules (nuclear acids, DNA and RNA, proteins etc) unifying one more the linkage between Science and Art.
Data set of the week: (2011/06/13)
A comprehensive map of the human urinary proteome. Overall rating: 
 This data set was made available as three (3) multidimensional chromotography experiments, resulting in 28 analysis sets,
including 3 summary runs.
The data was published by
Marimuthu A, O'Meally RN, Chaerkady R, Subbannayya Y, Nanjappa V, Kumar P, Kelkar DS, Pinto SM, Sharma R, Renuse S, Goel R, Christopher R, Delanghe B, Cole RN, Harsha HC, and Pandey A. in
J Proteome Res. 2011 10:2734-43 (PubMed).
This data set was made available as three (3) multidimensional chromotography experiments, resulting in 28 analysis sets,
including 3 summary runs.
The data was published by
Marimuthu A, O'Meally RN, Chaerkady R, Subbannayya Y, Nanjappa V, Kumar P, Kelkar DS, Pinto SM, Sharma R, Renuse S, Goel R, Christopher R, Delanghe B, Cole RN, Harsha HC, and Pandey A. in
J Proteome Res. 2011 10:2734-43 (PubMed).
If you have any interest in developing a diagnostic test that uses human urine, you should
take a good close look at the data in this study. The investigators used the most up-to-date techniques (Orbitrap-Velos using HCD)
and one important type of protein fractionation (lectin pull-down). The results give quite a clear picture
of the major and minor proteins present in urine and its provides a nice map to the peptides and modifications
that can be expected from this important class of clinical samples.
Data set of the week: (2011/06/06)
Proteomics analysis of the cardiac myofilament subproteome reveals dynamic alterations in phosphatase subunit distribution. Overall rating: 
 This data set was made available as 156 individual LC/MS/MS runs,
each representing an SDS-PAGE gel band.
The data was published by
Yin X, Cuello F, Mayr U, Hao Z, Hornshaw M, Ehler E, Avkiran M, and Mayr M. in
Mol Cell Proteomics, 2010, 9:497-509 (PubMed).
This data set was made available as 156 individual LC/MS/MS runs,
each representing an SDS-PAGE gel band.
The data was published by
Yin X, Cuello F, Mayr U, Hao Z, Hornshaw M, Ehler E, Avkiran M, and Mayr M. in
Mol Cell Proteomics, 2010, 9:497-509 (PubMed).
This study provides some interesting insights into the protein composition of rat
cardiac myocytes, both in control and treated cases. The data clearly supports the conclusions in the
paper and it also provides many of the best observations of the cardiac muscle proteins associated with
these cells. There has been significantly less attention to rat proteomics than to mouse or human, so
quality data sets such as this one significantly improve what is known about this important model species.
Data set of the week: (2011/05/30)
Novel In Situ Collection of Tumor Interstitial Fluid from a Head and Neck Squamous Carcinoma Reveals a Unique Proteome with Diagnostic Potential. Overall rating: 
 This data set was composed from multiple LC/MS/MS run using multidimenstional chromatography into single
summary result.
The data was published by
Stone MD, Odland RM, McGowan T, Onsongo G, Tang C, Rhodus NL, Jagtap P, Bandhakavi S, and Griffin TJ. in
Clin Proteomics 2010 6:75-82 (PubMed).
This data set was composed from multiple LC/MS/MS run using multidimenstional chromatography into single
summary result.
The data was published by
Stone MD, Odland RM, McGowan T, Onsongo G, Tang C, Rhodus NL, Jagtap P, Bandhakavi S, and Griffin TJ. in
Clin Proteomics 2010 6:75-82 (PubMed).
These results give an excellent insight into the proteins that can be
expected in interstitial fluid, a clinically important fluid that has not been studied extensively by proteomics
methods. The composition of the fluid was most similar to blood plasma and plasma-derived fluids, e.g. saliva,
urine or cerebrospinal fluid. Anyone planning to do an experiment involving interstitial fluid should
examine these results carefully.
Data set of the week: (2011/05/24)
Proteomic analysis reveals a virtually complete set of proteins for translation and energy generation in elementary bodies of the amoeba symbiont Protochlamydia amoebophila. Overall rating: 
 This data was collected from a combination of multidimensional chromatography and SDS-PAGE bands, resulting in 232
individual data sets.
The data was published by
Sixt BS, Heinz C, Pichler P, Heinz E, Montanaro J, Op den Camp HJ, Ammerer G, Mechtler K, Wagner M, and Horn M. in
Proteomics, 2011, 11:1868-92 (PubMed).
This data was collected from a combination of multidimensional chromatography and SDS-PAGE bands, resulting in 232
individual data sets.
The data was published by
Sixt BS, Heinz C, Pichler P, Heinz E, Montanaro J, Op den Camp HJ, Ammerer G, Mechtler K, Wagner M, and Horn M. in
Proteomics, 2011, 11:1868-92 (PubMed).
The results presented in this paper consistuted the first proteomics information available
about an ameobiod obligate symbiont of the Acanthamoeba spp.
These common amoeba are only rarely pathogenic, however studying their symbiont's metabolism may provide
insight into the molecular basis of the eukaryote/prokaryote endosymbyotic relationships that seem to be very common in nature. The recent availability of
the symbiont's genome made the use of proteomics techniques possible. The combination of methods used in this
study were a little unusual, but they resulted in a good survey of the proteins in the organism, adding
1447 P. amoebophila proteins
to GPMDB.
 The GPM user community has a range of preferences when it comes to selecting which browser they
like to use for viewing proteomics information. The graph below shows the fraction of user sessions
on GPMDB as a function of the browser employed, in the period April 16 – May 17, 2011. Firefox
is clearly the most frequently used browser, with Internet Explorer and Chrome in second and third place, respectively.
The GPM user community has a range of preferences when it comes to selecting which browser they
like to use for viewing proteomics information. The graph below shows the fraction of user sessions
on GPMDB as a function of the browser employed, in the period April 16 – May 17, 2011. Firefox
is clearly the most frequently used browser, with Internet Explorer and Chrome in second and third place, respectively.
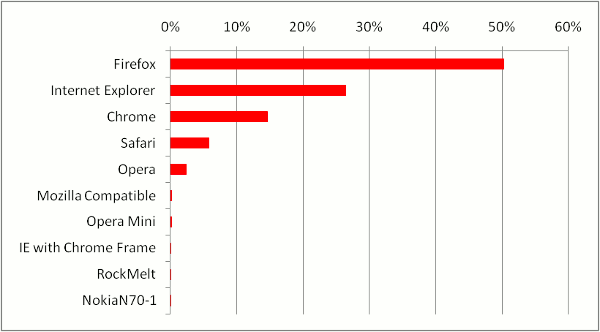
 A manuscript has been published in MCP by the HUPO group that has established the chromosome-centric
Human Proteome project. The full text of the article
is
available on line. From its Abtract:
A manuscript has been published in MCP by the HUPO group that has established the chromosome-centric
Human Proteome project. The full text of the article
is
available on line. From its Abtract:
... Given the presence of about 30% undisclosed proteins out of 20,300 protein gene products,
a systematic global effort is necessary to achieve this goal with respect to protein abundance,
distribution, subcellular localization, interaction with other biomolecules, and functions at
specific time points. As a general experimental strategy, HPP groups employ the three working
pillars for HPP: mass spectrometry, antibody capture, and bioinformatics tools and knowledge base.
The HPP participants will take advantage of the output and cross-analyses from the ongoing HUPO initiatives
and a chromosome-based protein mapping strategy, termed C-HPP with many national teams currently engaged ...
Data set of the week: (2011/05/15)
Multi-omics approach to study the growth efficiency and amino acid metabolism in Lactococcus lactis at various specific growth rates. Overall rating: 
 This data was collected from multidimensional chromatography, resulting in 64
LC MS/MS runs and experiment summaries.
The data was published by
Lahtvee PJ, Adamberg K, Arike L, Nahku R, Aller K, and Vilu R. in
Microbial Cell Factories, 2011, 10:12. (PubMed).
This data was collected from multidimensional chromatography, resulting in 64
LC MS/MS runs and experiment summaries.
The data was published by
Lahtvee PJ, Adamberg K, Arike L, Nahku R, Aller K, and Vilu R. in
Microbial Cell Factories, 2011, 10:12. (PubMed).
This study was an outstanding example of the application of proteomics methods carefully
and methodically to a problem in biotechnology. All of the aspects of the investigation — experimental design, sample preparation,
chromatography and mass spectrometry — were well thought out and executed with a consistent attention
to detail and quality. The experiments reported in the paper go well beyond simply performing proteomics experiments by the use of other 'omics approaches,
significantly increasing the value of the proteomics results. The information generated by this study has greatly expanded general knowledge with regards to the proteome of
Lactococcus lactis, one of the most important bacteria in the food processing industry. It
also provides a good basis for understanding aspects of this organism's metabolism.
 From the HUPO website:
From the HUPO website:
HUPO and HUPO Industry Advisory Board (IAB) are pleased to announce that the nomination period for
the new “HUPO Science Technology Award” is now open.
The technical award should be presented at the HUPO Annual World Congress to an individual whose
contributions drove a proteomic based technological product or procedure to commercial success.
The industrial based individual should be a key player in the commercialization (either R&D or
marketing) of a proteomics based technology (but does not necessarily have to be the original
inventor). Although academic settings often provide initial design of a new technology or technique, this
award is intended to pay recognition to the industrial partnership that developed a proteomic
based tool or application into a format that allows the advancement of the whole scientific community.
 During the daily data update, GPMDB surpassed the 300,000,000 mark for peptide identifications. We would like
to thank all of our contributors for making this achievement possible. We would also like to thank all
of the individuals that have contributed data to our sister projects — TRANCHE, PeptideAtlas, and
PRIDE — which we have been able to import and make available in GPMDB. Special thanks goes to
Proteome Software for their long term
support of this project.
During the daily data update, GPMDB surpassed the 300,000,000 mark for peptide identifications. We would like
to thank all of our contributors for making this achievement possible. We would also like to thank all
of the individuals that have contributed data to our sister projects — TRANCHE, PeptideAtlas, and
PRIDE — which we have been able to import and make available in GPMDB. Special thanks goes to
Proteome Software for their long term
support of this project.
Data set of the week: (2011/05/08)
Large-scale label-free quantitative proteomics of the pea aphid-Buchnera symbiosis. Overall rating: 
 This data was collected from excised SDS-PAGE gel bands, resulting in 148
LC MS/MS runs.
The data was published by
Poliakov A, Russell CW, Ponnala L, Hoops HJ, Sun Q, Douglas AE, and van Wijk KJ in
Mol Cell Proteomics, 2011 Mar 18 (PubMed).
This data was collected from excised SDS-PAGE gel bands, resulting in 148
LC MS/MS runs.
The data was published by
Poliakov A, Russell CW, Ponnala L, Hoops HJ, Sun Q, Douglas AE, and van Wijk KJ in
Mol Cell Proteomics, 2011 Mar 18 (PubMed).
These experiments explore the proteomics of the relationship between the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum,
and its endosymbiont bacterium Buchnera aphidicola.
Buchnera bacteria are obligate endosymbionts in aphids, having lost the metabolic pathways necessary to be free living organisms.
The recent availability of the genomes of both the aphid and the bacterium makes it possible to do a thorough job of examining
the proteins present from both genomes in the intact organism. The results clearly demonstrate that any investigation of insect proteomics should be very
mindful of selecting an appropriate mixture of proteomes when analyzing raw data. This data set should also be
revisited when the genomes of other secondary endosymbionts of the pea aphid become known, such as
Hamiltonella defensa, Regiella insecticola, and Serratia symbiotica.
 The Human Proteome Organization (HUPO) has released some documents describing
the current draft plans for the Human Proteome Project. The main document (doc)
was a brief summary of the decisions made at the meeting, and an associated set of slides (pdf)
shows how the group has distilled down the idea of how such a project could be organized, along with a proposed
set of project goals/milestones.
The Human Proteome Organization (HUPO) has released some documents describing
the current draft plans for the Human Proteome Project. The main document (doc)
was a brief summary of the decisions made at the meeting, and an associated set of slides (pdf)
shows how the group has distilled down the idea of how such a project could be organized, along with a proposed
set of project goals/milestones.
From the HUPO web site: A workshop took place in Busan (Korea) on March 30, 2011 for the creation of the HPP consortium.
A short summary of the discussion is provided, followed by the recommendations and decisions forwarded
to the HUPO Executive committee that validated these decisions on April 5, 2011.
Data set of the week: (2011/05/01)
Large-scale Arabidopsis phosphoproteome profiling reveals novel chloroplast kinase substrates and phosphorylation networks. Overall rating: 
 This data was collected and deposited as 13
LC MS/MS runs, using a metal oxide column strategy to enrich phosphopeptides.
The data was published by
Reiland S, Messerli G, Baerenfaller K, Gerrits B, Endler A, Grossmann J, Gruissem W, and Baginsky S. in
Plant Physiol. 2009 150:889-903 (PubMed).
This data was collected and deposited as 13
LC MS/MS runs, using a metal oxide column strategy to enrich phosphopeptides.
The data was published by
Reiland S, Messerli G, Baerenfaller K, Gerrits B, Endler A, Grossmann J, Gruissem W, and Baginsky S. in
Plant Physiol. 2009 150:889-903 (PubMed).
This study was a very successful application of the prefractionation techniques that
have been developed to enrich phosphopeptides. The detailed examination of plant phosphoproteomics has been well behind fungal (yeast)
and animal (human/mouse) studies, but this series of experiments shows conclusively that the same methods
can be used to great effect. The data was of sufficient quality to allow the identification of more than 2,000 phosphopeptides per run. The identifications
show the enrichment of acidic residues characteristic of metal oxide enrichment schemes.
The displayed information for proteins sourced from the US NCBI has been augmented by the
addition of Conserved
Domains Database (CDD) information to the display
(from the example
GPM64300013159):

The domain information is displayed immediately below the protein's text description
line. Each domain is linked back to CDD for additional information and an exerpt of the domain's description
is also displayed. A more detailed version of this information is available for each protein by clicking
on the "protein" link and reading the NCBI information sheet at the bottom of the page. If there are multiple examples
of a specific domain in a protein, the CCD link is followed by the number of times that domain is repeated. The CDD
information will be displayed for all proteins with "gi"-type accession numbers.
 This data was composed of 125
LC MS/MS runs, generated from SDS-PAGE bands.
The data was published by
Chik JK, Schriemer DC, Childs SJ, and McGhee JD in
J Proteome Res. 2011 Apr 15 (PubMed).
This data was composed of 125
LC MS/MS runs, generated from SDS-PAGE bands.
The data was published by
Chik JK, Schriemer DC, Childs SJ, and McGhee JD in
J Proteome Res. 2011 Apr 15 (PubMed).
The results of this study demonstrated the importance of examining specific tissues
in an organism, even one with as few differentialed organ systems as C. elegans. Even though C. elegans
is well represented in GPMDB (> 1,000,000 protein ids), this study contains many top ranking identifications
for specific proteins, almost certainly because of the relatively high concentration of those proteins in the oocyte. The
data itself was taken in a very consistent manner, with each gel band having good correlation between the detected
gene product molecular masses. With 6,691 total protein ids, this rather modest study provides a very
comprehensive view of the C. elegans oocyte proteome.
Data set of the week: (2011/04/17)
Identification of outer membrane proteins from an Antarctic bacterium Pseudomonas syringae Lz4W. Overall rating: 
 The data from this study was comprised of 14
LC MS/MS runs, generated from SDS-PAGE bands.
The data was published by
Jagannadham MV, Abou-Eladab EF, and Kulkarni HM in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 Mar 29 (PubMed).
The data from this study was comprised of 14
LC MS/MS runs, generated from SDS-PAGE bands.
The data was published by
Jagannadham MV, Abou-Eladab EF, and Kulkarni HM in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 Mar 29 (PubMed).
This study demonstrates how to gain significant insights into prokaryotic cell organization
using proteomics techniques, once you have a good genome sequence for a closely related species (or two). The species
under study here was a plant pathogen — Pseudomonas syringae —
that has the singular ability to elevate the freezing point of water. This paper focuses on a cryophilic
strain of the bacteria in an attempt to understand how it can function effectively in a rather extreme environment.
The authors do a good job of using a proteomics strategy to acquire useful information about the organism's biology.
Data set of the week: (2011/04/10)
Improved Peptide Identification by Targeted Fragmentation Using CID, HCD and ETD on an LTQ-Orbitrap Velos. Overall rating: 
 The experiments in this study generated 73
LC MS/MS runs, using single- and multi-dimensional chromatographic peptide separations.
The data was published by
Frese CK, Altelaar AF, Hennrich ML, Nolting D, Zeller M, Griep-Raming J, Heck AJ, and Mohammed S in
J Proteome Res. 2011 Apr 1 (PubMed).
The experiments in this study generated 73
LC MS/MS runs, using single- and multi-dimensional chromatographic peptide separations.
The data was published by
Frese CK, Altelaar AF, Hennrich ML, Nolting D, Zeller M, Griep-Raming J, Heck AJ, and Mohammed S in
J Proteome Res. 2011 Apr 1 (PubMed).
These results were produced by a well thought-out study to determine
the validity of various claims that have been made about the efficacy of the three most
popular fragmentation modalities for MS/MS-based proteomics: CID, ETD and HCD. Each
of these mechanisms was given a good workout and a fair, side-by-side comparison was
made without apparent bias. If you are interested in selecting between one of these
methods for an upcoming experiment, it would be well worth your while to look at this
comparative study to assist you in making up your own mind.
 The British Society for Proteome Research has started a
discussion forum
to determine interest in Great Britain's involvement in the global
Human Proteome Project effort. Anyone
with an opinion should join the discussion. From this site:
The British Society for Proteome Research has started a
discussion forum
to determine interest in Great Britain's involvement in the global
Human Proteome Project effort. Anyone
with an opinion should join the discussion. From this site:
Several countries have already signed up, including Australia, Canada, China, Japan, Russia,
South Korea, Sweden, Switzerland and the USA, and it is under active consideration elsewhere,
e.g. in France and Germany. There may be some major scientific advantages in participation but, equally,
there may be opportunity costs.
Additionally, gene-, protein- and disease-centric strategies for the HPP have been proposed
but their relative merits need to be considered.
Data set of the week: (2011/04/03)
A proteogenomic analysis of Anopheles gambiae using high-resolution Fourier transform mass spectrometry. Overall rating: 
 The experiments in this study generated 335
LC MS/MS runs, most representing individual SDS-PAGE gel bands.
The data was made available in Tranche by
Raghothama Chaerkady, Dhanashree S. Kelkar, Babylakshmi Muthusamy, Kumaran Kandasamy,
Sutopa B. Dwivedi, Nandini Patankar, Min-Sik Kim1, Santosh Renuse,
Sneha Pinto, Rakesh Sharma, Harsh Pawar, Ajeet Kumar Mohanty, Yi Yang,
A.P. Dash, Robert M. MacCallum, Bernard Delanghe, Ashwani Kumar,
Godfree Mlambo, Mobolaji Okulate, Nirbhay Kumar, and Akhilesh Pandey.
The experiments in this study generated 335
LC MS/MS runs, most representing individual SDS-PAGE gel bands.
The data was made available in Tranche by
Raghothama Chaerkady, Dhanashree S. Kelkar, Babylakshmi Muthusamy, Kumaran Kandasamy,
Sutopa B. Dwivedi, Nandini Patankar, Min-Sik Kim1, Santosh Renuse,
Sneha Pinto, Rakesh Sharma, Harsh Pawar, Ajeet Kumar Mohanty, Yi Yang,
A.P. Dash, Robert M. MacCallum, Bernard Delanghe, Ashwani Kumar,
Godfree Mlambo, Mobolaji Okulate, Nirbhay Kumar, and Akhilesh Pandey.
These experiments were a tour de force of how to study
whole organism proteomics in insects. The organism was disected and important
organ systems were studied in detail. Even though the A. gambiae genome
has been available since 2002, this study was the first thorough examination of
the distribution of proteins in this important mosquito (it is the insect vector
of malaria). Technically, it uses cutting edge mass spectrometry-based identification
methods. The measured fragment ion mass accuracy was < 5 ppm for most of the individual
runs, allowing for high confidence peptide identifications (≤ 0.05% FPR).
 From the ProteomExchange: Events site:
From the ProteomExchange: Events site:
ProteomeXchange informal meeting, where the project stakeholders would also be
invited to attend and talk. The idea is to discuss open issues such as the
expected data workflow or exchange formats. -
Friday April 15th: ProteomeXchange formal kickoff meeting.
For members of the consortium only. The idea is also, at least for some of the
stakeholders, to have some more focused meetings in the late afternoon-evening.
- Saturday April 16th: ProteomeXchange stakeholders meeting.
The idea is that it would be possible to fly back on the early evening.
 From HUPO 2011 co-chair Jean-Charles Sanchez:
From HUPO 2011 co-chair Jean-Charles Sanchez:
We just decided that the website will remain open until 4 April. It will not be advertised
specifically other than the text which is currently
on the website
where we will change the date from 20 March to 4 April.
On 18 April we will open a system for submission for late breaking abstracts (posters only)
until probably July. This new opening will be announced by HUPO, EuPA and SPS to
their members in a mailing.
 The experiments in this study generated 306
LC MS/MS runs. This data set was made available as 32 separate TRANCHE entries, credited to
Regine M Schoenherr from Mandy Paulovich's laboratory at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center
in Seattle. The data was published by
Schoenherr, R. M., Kelly-Spratt, K. S., Lin, C., Whiteaker, J. R., et al.
in Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2011, 5, 179-188 (Abstract).
The experiments in this study generated 306
LC MS/MS runs. This data set was made available as 32 separate TRANCHE entries, credited to
Regine M Schoenherr from Mandy Paulovich's laboratory at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center
in Seattle. The data was published by
Schoenherr, R. M., Kelly-Spratt, K. S., Lin, C., Whiteaker, J. R., et al.
in Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2011, 5, 179-188 (Abstract).
Each of the individual experiments was derived from a set of 10 control and 10 tumour-bearing
Her2/Neu mice. These mice have been a popular model system for cancer research because of their
tendency to generate metastatic breast tumours. The results give a good profile of the proteins
detectable in M. musculus plasma under normal control conditions using standard methods and
the Thermo-Finnigan LTQ as the main detection platform. Each TRANCHE entry was entitled using
a mnemonic, for example:
"MARS_Sample_Pool_2_Normal_mzXML". This abbreviated form describes the protein handling (MARS depletion), the specific replicate (Sample_Pool_2) and the animal pool (Normal). The use of this type of mnemonic has become a wide-spread (but regretable) practice in the proteomics community for describing information deposited in repositories. Data set of the week: (2011/03/20)
An integrated workflow for charting the human interaction proteome: insights into the PP2A system.  The experiments in this study generated 62
LC MS/MS runs. Each run was the result of an affinity purification experiment, with either baits or controls.
The data was published by
Glatter T, Wepf A, Aebersold R, and Gstaiger M.
Mol Syst Biol. 2009;5:237. (PubMed).
The experiments in this study generated 62
LC MS/MS runs. Each run was the result of an affinity purification experiment, with either baits or controls.
The data was published by
Glatter T, Wepf A, Aebersold R, and Gstaiger M.
Mol Syst Biol. 2009;5:237. (PubMed).
These results clearly demonstrated the merits of using highly specific affinity purification experiments
when trying to thoroughly study the proteins associated with a specific pathway or particle.
The data was of good quality, although the ion source did not perform uniformly in the low-organic
phase portion of the liquid chromatography runs. For example, contrast the retention time vs pI plot for GPM33000032760 (good)
with GPM33000032731 (not as good).
This commonly seen experimental artifact probably had little effect on the
biological conclusions drawn from the results. However, if the same data was used
to draw inferences about which peptides were appropriate candidates for quantitation methods,
this ion source inconsistency would lead to a bias against early eluting peptides.
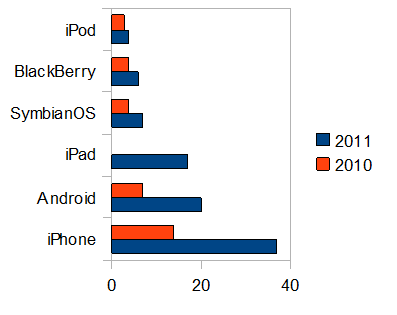 The graph to the left shows the number of user sessions accessing data in GPMDB for the period Jan. 1 - Mar. 15, in 2010 and
2011 by scientists with mobile wireless platforms. The total number of these sessions has increased by 3-fold and the mix of devices
used has changed. While the iPhone is still the most popular handset, the use of Android-powered devices and the iPad has
grown significantly. The use of SymbianOS and Blackberry handsets has also grown, but use of these older systems is clearly not keeping
pace with the growth associated with the more popular iOS and Android devices.
The graph to the left shows the number of user sessions accessing data in GPMDB for the period Jan. 1 - Mar. 15, in 2010 and
2011 by scientists with mobile wireless platforms. The total number of these sessions has increased by 3-fold and the mix of devices
used has changed. While the iPhone is still the most popular handset, the use of Android-powered devices and the iPad has
grown significantly. The use of SymbianOS and Blackberry handsets has also grown, but use of these older systems is clearly not keeping
pace with the growth associated with the more popular iOS and Android devices.
The current trends suggest that this type of platform is becoming an integral tool for accessing information
by biomedical researchers. GPM will be increasing its efforts to make interfaces that provide as much information as possible
in a form that is compatible with the requirements of these devices.
 The Human Proteome Organization 2011 10th World Congress
(September 4-7, Geneva Palexpo, CH 1218 Le Grand-Saconnex, Geneva, Switzerland)
has the following deadline coming up Wednesday (March 16, 2011):
The Human Proteome Organization 2011 10th World Congress
(September 4-7, Geneva Palexpo, CH 1218 Le Grand-Saconnex, Geneva, Switzerland)
has the following deadline coming up Wednesday (March 16, 2011):
 The Canadian National Proteomics Network's 2011 Conference (May 8-11, 2011, Banff Springs Hotel, Banff AB)
has the following deadlines coming up tomorrow (March 15, 2011):
The Canadian National Proteomics Network's 2011 Conference (May 8-11, 2011, Banff Springs Hotel, Banff AB)
has the following deadlines coming up tomorrow (March 15, 2011):
Data set of the week: (2011/03/13)
Primary tumor xenografts of human lung adeno and squamous cell carcinoma express distinct proteomic signatures.  The experiments in this study resulted in 30
MudPIT experiments. Each experiment was composed of four MudPIT fractions, along with a
summary of the set of fractions, a total of five GPM files per sample. The data was published by
Wei Y, Tong J, Taylor P, Strumpf D, Ignatchenko V, Pham NA, Yanagawa N, Liu G, Jurisica I, Shepherd FA, Tsao MS, Kislinger T, and Moran MF in
J Proteome Res. 2011 10:161-74. (PubMed).
The experiments in this study resulted in 30
MudPIT experiments. Each experiment was composed of four MudPIT fractions, along with a
summary of the set of fractions, a total of five GPM files per sample. The data was published by
Wei Y, Tong J, Taylor P, Strumpf D, Ignatchenko V, Pham NA, Yanagawa N, Liu G, Jurisica I, Shepherd FA, Tsao MS, Kislinger T, and Moran MF in
J Proteome Res. 2011 10:161-74. (PubMed).
The results give the proteins present in each of 10 human tumours grafted into SCID mice, with
three replicates per tumour. The analysis required the simultaneous use of both the mouse and human
proteomes, resulting in protein lists composed of a mixture of the two types of proteins. The human
proteins show the proteins that would normally be expected in human tumour tissue, as well as a normal
compliment of mouse blood proteins. In addition to the blood proteins, there was also clear evidence for
a set of murine extracellular matrix proteins. The presence of these proteins strongly suggest that
the host was able to begin infiltrating the tumour with ECM, even without a normal immune response to the xenograft material.
 Dr. Bill Hancock (Northeastern University) will be presenting a talk entitled "The Study of Human Chromosome 17,
Human Proteome Project (HPP)" at the US HUPO meeting to be held in Rayleigh, North Carolina.
The talk will lay out the US plans for studying C17 in detail. Dr. Hancock will discuss the
current state of proteomics knowledge associated with this chromosome as well as goals
for the project. The GPM endorses the US plan for Chromosome 17 and
it will provide as much assistance as possible to this project.
Dr. Bill Hancock (Northeastern University) will be presenting a talk entitled "The Study of Human Chromosome 17,
Human Proteome Project (HPP)" at the US HUPO meeting to be held in Rayleigh, North Carolina.
The talk will lay out the US plans for studying C17 in detail. Dr. Hancock will discuss the
current state of proteomics knowledge associated with this chromosome as well as goals
for the project. The GPM endorses the US plan for Chromosome 17 and
it will provide as much assistance as possible to this project.
 The GPM interface allows users to associate ontology
terms with search results. We have recently updated the BRENDA cell type list to include 2,200 new descriptions
and for the first time added the PSI-MS ontology terms comprised of 1,200 mass spectrometry-specific
controlled vocabulary phrases for characterizing experimental conditions. To be sure that you are using
the new lists, please use the "reload" button when you browse to your favorite GPM search page.
The GPM interface allows users to associate ontology
terms with search results. We have recently updated the BRENDA cell type list to include 2,200 new descriptions
and for the first time added the PSI-MS ontology terms comprised of 1,200 mass spectrometry-specific
controlled vocabulary phrases for characterizing experimental conditions. To be sure that you are using
the new lists, please use the "reload" button when you browse to your favorite GPM search page.
The purpose of these ontology terms is to aid the identification of data sets of interest at a later
time. By standardizing the terminology associated with data in GPMDB, the process of retrieving
useful information associated with a particular biological/analytical context becomes easier.
Data set of the week: (2011/03/06)
The ubiquitin-proteasome system is a key component of the SUMO-2/3 cycle.  The experiments in this study resulted in 5
LC/MS/MS runs. The data was published by
Schimmel J, Larsen KM, Matic I, van Hagen M, Cox J, Mann M, Andersen JS, and Vertegaal AC in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2008 7:2107-22 (PubMed).
The experiments in this study resulted in 5
LC/MS/MS runs. The data was published by
Schimmel J, Larsen KM, Matic I, van Hagen M, Cox J, Mann M, Andersen JS, and Vertegaal AC in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2008 7:2107-22 (PubMed).
The data in this study resulted from a series of pull-down experiments with SILAC quantitation using
HeLa cells. The results contained an unusually large number of identifications for rare proteins, as well as
an over-representation of identifications that rated in the top percentile of all id's for particular proteins.
Analysis of the protein sequence motifs present showed that the RNA recognition motif, RNP-1
had been highly enriched by this particular pull-down strategy.
The underlying peptide id's were top quality with a very low number of false positives in the reported
sequences assignments.
 The final planning workshop for the Canadian Human Proteome Project will be
held in conjunction with the spring meeting of the CNPN,
at the Banff Springs Hotel, Alberta, CA. The workshop is scheduled for
the last day of the conference (May 11, 2010).
The final planning workshop for the Canadian Human Proteome Project will be
held in conjunction with the spring meeting of the CNPN,
at the Banff Springs Hotel, Alberta, CA. The workshop is scheduled for
the last day of the conference (May 11, 2010).
The results of this workshop will define
the character of Canada's contribution to the Human Proteome Project, e.g.,
the chromosome chosen (probably C6 or C21), the technologies to be employed, as
well as the estimated cost and the number of groups required for this cross-country
collaborative effort.
 Many researchers are still using the obsolete International Protein Index sequence
sets for their proteomics analysis. Because IPI is no longer officially supported by
EBI, we have set up a segment of our FTP site to archive the IPI FASTA files and
associated annotation. You can retrieve these files at ftp://ftp.thegpm.org/fasta/ipi.
Many researchers are still using the obsolete International Protein Index sequence
sets for their proteomics analysis. Because IPI is no longer officially supported by
EBI, we have set up a segment of our FTP site to archive the IPI FASTA files and
associated annotation. You can retrieve these files at ftp://ftp.thegpm.org/fasta/ipi.
 The experiments in this study resulted in 99
LC/MS/MS runs. The data was published by
Burkard TR, Planyavsky M, Kaupe I, Breitwieser FP, Bürckstümmer T, Bennett KL, Superti-Furga G, and Colinge J. in
BMC Syst Biol. 2011 5:17 (PubMed).
The experiments in this study resulted in 99
LC/MS/MS runs. The data was published by
Burkard TR, Planyavsky M, Kaupe I, Breitwieser FP, Bürckstümmer T, Bennett KL, Superti-Furga G, and Colinge J. in
BMC Syst Biol. 2011 5:17 (PubMed).
The purpose of this research was to compare the proteomes of six human cell lines and determine
which candidate proteins were present in all six. This set of proteins they postulated to be a "central"
proteome: those proteins required by all human cells. While this concept will be debated for some time,
this study provides excellent insight into the proteins present in
these 6 cell lines under controlled conditions. The data divided up by cell lines are as follows:
 The Canadian National Proteomics Network
(Canada's HUPO affilate) has released its initial planning document for a human proteome project
(pdf version).
The document suggests the possibility that perhaps Canada's role in the wider HUPO-lead project
may be the detailed analysis of proteins from Chromosome 6 or Chromosome 21. No further information
regarding timing, goals or methods to be employed has been made available.
The Canadian National Proteomics Network
(Canada's HUPO affilate) has released its initial planning document for a human proteome project
(pdf version).
The document suggests the possibility that perhaps Canada's role in the wider HUPO-lead project
may be the detailed analysis of proteins from Chromosome 6 or Chromosome 21. No further information
regarding timing, goals or methods to be employed has been made available.
As a result of Peptidome's closing, some of the links associated with
results in GPMDB from Peptidome-sourced spectra would have become non-functional. To
ensure continuity of information, we have set up an alternate site for the experiment
and project information that would normally be obtained from Peptidome. All of the
links in GPMDB have been updated to point to this new resource.
To use this alternate annotation resource, a simple link can be used. For example, experiment
PSM1250 or project PSE132 can be accessed by the respective links:
This study contains two
experiments. The data was imported from Peptidome and was published by
Ettwig KF, Butler MK, Le Paslier D, Pelletier E, Mangenot S, Kuypers MM, Schreiber F, Dutilh BE, Zedelius J,
de Beer D, Gloerich J, Wessels HJ, van Alen T, Luesken F, Wu ML, van de Pas-Schoonen KT, Op den Camp HJ,
Janssen-Megens EM, Francoijs KJ, Stunnenberg H, Weissenbach J, Jetten MS, and Strous M in
Nature. 2010 464:543-8 (PubMed).
The data was generated using lysed cells from an unusual anaerobic bacterium, referred to by
NCBI as "NC10 bacterium 'Dutch sediment'". The sample itself was obtained from mud dug out of a
ditch in Holland. Compared to the well-controlled studies done with lab strains of bacteria or
cell lines, the researchers in this case dealt with generating identifiable proteins from real field samples. The
genome of the dominant species (Candidatus Methylomirabilis oxyfera) was available and the data could be
interpreted in light of an unusual feature of the organism's methane oxidation metabolism.
The European Proteomics Association has just published its 4th
informational bulletin
(get it here). It has a nice summary of the status of various projects in
Europe. Congratulations to Jean-Charles Sanchez and György Marko-Varga for their elections to
be EuPA Vice-President and President, respectively.
From the Peptidome website:
Due to budgetary constraints NCBI will be discontinuing the Peptidome Repository.
Over the next few weeks, we will phase out the online browser, query, and display
interfaces.
All existing data and metadata files will continue to be made available from our ftp
server ftp://ftp.ncbi.nih.gov/pub/peptidome/ indefinitely. Those files are named
according to their Peptidome accession number, allowing cited data to still be
identified and downloaded. Furthermore, we will endeavor to deposit all
Peptidome data in a different public mass spectrometry repository;
information about this effort will follow soon.
For those datasets that have been accessioned, but have not yet been made public, submitters have the option of withdrawing the data now and moving it to another repository. If we retain the data, it will move to the Peptidome FTP site on the date at which it is currently designated to go public. Data set of the week: (2011/02/13)
Identification of cell wall and cytoplasmic proteins of Aspergillus fumigatus. This study contains one summary
of LC/MS/MS runs. The data sets were obtained from a whole organism extract using a Thermo-
Finnegan LTQ mass spectrometer. The results have not be published, but were made available
through Peptidome, sample PSM1346.
Aspergillus fumigatus is a commonly occuring environmental saphrophytic fungus. It can
become clinically important in individuals with suppressed immune systems. The MS/MS data was
typical of LTQ-based analysis, but the results obtained from the data was a bit of a puzzle. The
original analysis (in Peptidome) only reported identifications for 2,223 spectra, whereas
a fairly straighforward analysis in our hands yielded approximately 20,000 identifications. While
the parameters used in the Peptidome analysis were not optimized (particularly the parent
ion mass tolerance and the list of variable modifications), repeated examination and re-analysis
in our hands was unable to resolve this significant difference. The data annotation stored in GPMDB
was performed twice: once with the CADRE
protein sequences alone and again with CADRE + RefSeq sequences for the same fungus strain. Because the
original MASCOT analysis was made available on Peptidome's FTP site, it was possible to
annotate each spectrum in the GPMDB analysis with those results for comparison (these appear as
comments on each of the spectrum display pages).
The CNPN is promoting a Canadian Human Proteomics Project (CHPP), which will be
developed during a Toronto-based Workshop (February 22, 2011) and a
Vancouver-based Workshop (date to be announced). CNPN invites you to participate
and provide feedback on the first draft of the CHPP Position Paper.
Further details on the Toronto Workshop can be found at www.cnpn.ca,
including an agenda outlining presentations and speakers.
Breakout sessions will allow the community to address critical components of CHPP
and develop strategies for integration into a White Paper. The White Paper
will be presented to the scientific community and funding agencies at the
CNPN Annual Symposium, May 8-11th, in Banff, Alberta.
This study contains 118
LC/MS/MS runs. The data sets were a combination of gel band and multidimensional chromatography
separations. The mass spectrometry appears to have been performed using HCD fragmentation
with an Orbitrap-LTQ hybrid instrument.
This data has not yet been published.
The results obtained from this data serve as a primer on what can be obtained
from the proteomics analysis of Leishmania major,
a trypanosomatid protozoan that causes leishmaniasis.
The data was generated from the two dominant life stages of the organism: the amastigote stage
that is adopted in the mammalian host; and the promastigote stage, adopted in the insect vector. The
combination of protein-level and peptide-level separation as well as the very high accuracy fragment
ion mass measurements make for a very broad coverage of proteins and peptides. Anyone interested
in the proteomics of L. major should study these results thoroughly before planning their
own experiments.
The daily incremental update of GPMDB has brought the total number of spectra
assigned to peptide sequences up to 253,866,646. For the last 6 years the number
of assigned spectra available has doubled year-over-year and it would appear that
this trend is continuing. Thanks to all of our search site users as well as all of
the laboratories that have made their data available through other sites, such as
TRANCHE, PRIDE and Peptidome.
Data set of the week: (2011/01/30)
The steady-state repertoire of human SCF Ubiquitin ligase complexes does not require ongoing Nedd8 conjugation. This study contains 41
LC/MS/MS runs.
This data was published in
Lee JE, Sweredoski MJ, Graham RL, Kolawa NJ, Smith GT, Hess S, and Deshaies RJ.,
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010 Dec 17 (PubMed).
These interesting experiments were performed to explore the details of the current
model of how intracellular protein degradation is organized and regulated. The
experiments used SILAC and non-SILAC quantitation methods and experimental techniques that
did a good job of pulling out the relavent cellular machinery. The results contained
the most detailed observations yet of some of the important proteins in the
ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation pathway, such as CAND1, CUL1, and the COPS subunits.
This study contains 19
LC/MS/MS runs.
This data has not been published, but was made available by Mastrobuoni, G, et al.,
through Tranche,
along with a few experimental details.
This data was very high quality, using isoelectric focussing to separate peptides in a similar
manner to the use of SCX in MudPit. The organism studied was Schmidtea mediterranae, which
is a free-living planarian (flatworm) with an exceptional ability to self regenerate when injured.
While there is a genome project underway for this organism, the proteome sequence has not been
made available. As an alternative, RNA sequence information was used, based on the
current version of Unigene. The results
show how well data can be analyzed with assembled transcriptional sequences only, which may remain
the best alternative for many species of zoological or botanical interest
for some years to come.
This study contains 6
LC/MS/MS runs, generated from HPLC experiments.
This data has not been published, but was made available by Taejoon Kwon, et al
on the Marcotte Lab web site's data section, under the heading Data_12 (see the
experimental description link for details).
This study provides a good view of the proteome of an important pathogen, Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
P. aeruginosa is a common free-living bacteria that can rapidly colonize human tissue if it has been
damaged or if there is a defect in the immune system. The results represent two biological replicates of cultured
cells and provides a good starting point for any study of proteins produced by this organism.
Data set of the week: (2011/01/02)
The leukocyte nuclear envelope proteome varies with cell activation and contains novel transmembrane proteins that affect genome architecture. This study contains 8
summary results, generated from multidimensional chromatography experiments.
The manuscript describing this work was published by
Korfali N, Wilkie GS, Swanson SK, Srsen V, Batrakou DG, Fairley EA, Malik P, Zuleger N, Goncharevich A, de Las Heras J, Kelly DA, Kerr AR, Florens L, and Schirmer EC,
Mol Cell Proteomics 2010 Dec;9:2571-85
(PubMed).
The results of this study provide a good survey contrasting the proteins present in R. norvegicus
and H. sapiens microsomes. The GO displays for the individual experiments demonstrate the quality of the
preparation methods used, showing very significant enrichment of endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi aparatus, integral membrane,
mitochondrion and other membrane associated subcellular structures.
Copyright © 2011, The Global Proteome Machine Organization
|